前言
在不远的将来,实现一定程度上的语音支持将成为日常科技的基本要求,整合了语音识别的python程序提供了其他技术无法比拟的交互性和可访问性。最重要的是,在python程序中实现语音识别非常简单。整个代码实现下来还不到150行。
原理简介
许多现代语音识别系统会在HMM识别之前使用神经网络,通过特征变换和降维技术来简化语音信号,也可以使用语音活动检测器将音频信号减少到可能包含语音的部分。
幸运的是,对于python来讲,一些语音识别的服务可通过API在线使用,且其中大部分也提供了Python SDK。
本文做的聊天机器人是基于百度语音识别和图灵机器人二者之上共同实现的。大致的流程如下图:
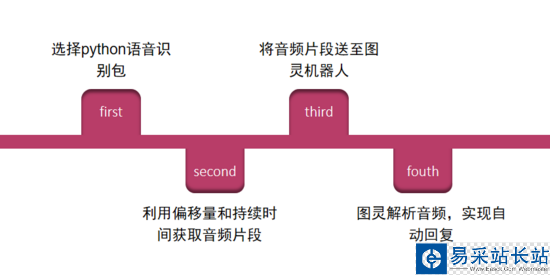
原理流程图.PNG
这里需要用的模块库有 requests、time、datetime、pyaudio、wave、aipspeech 等。
话不多说,上代码:
##@氢立方 2018.0911import requestsimport timeimport pygamefrom datetime import datetimefrom aip import AipSpeechfrom pyaudio import PyAudio,paInt16import waveimport osframerate=8000NUM_SAMPLES=2000channels=1sampwidth=2TIME=2def save_wave_file(filename,data): '''save the date to the wavfile''' wf=wave.open(filename,'wb') wf.setnchannels(channels) wf.setsampwidth(sampwidth) wf.setframerate(framerate) wf.writeframes(b"".join(data)) wf.close()def my_record(): pa=PyAudio() stream=pa.open(format = paInt16,channels=1, rate=framerate,input=True, frames_per_buffer=NUM_SAMPLES) my_buf=[] count=0 while count<TIME*6:#控制录音时间 string_audio_data = stream.read(NUM_SAMPLES) my_buf.append(string_audio_data) count+=1 print('.') save_wave_file('0001.wav',my_buf) stream.close()##def play():## wf=wave.open(r"D:/41125.mp3",'rb')## p=PyAudio()## stream=p.open(format=p.get_format_from_width(wf.getsampwidth()),channels=## wf.getnchannels(),rate=wf.getframerate(),output=True)## while True:## data=wf.readframes(chunk)## if data=="":break## stream.write(data)## stream.close()## p.terminate()##这里大家需要改成自己的ID和KEYAPP_ID = '11****843'API_KEY = '3Mnv***8**88******GbXa'SECRET_KEY = '147***8*88****1227684'aipSpeech = AipSpeech(APP_ID, API_KEY, SECRET_KEY)def getText(url): text = requests.post(url).json() return text['text']####key = '6ddc57c5761a4c62a30ea840e5ae163f'#api = 'http://www.tuling123.com/openapi/api?key=' + key +'&info ='key = '8b005db5f57556fb96dfd98fbccfab84' api = 'http://www.tuling123.com/openapi/api?key=' + key + '&info=' ##while True: ## info = input("我说/n") ## chunk=2014 my_record() print("录音完成") def get_file_content(filePath): with open(filePath,'rb') as fp: return fp.read() a = aipSpeech.asr(get_file_content('0001.wav '),'wav',8000,{}) print(a) b = str(a['result']) info = b url = api + info #print(url) text_01 = getText(url) print("机器人回/n",text_01) now = datetime.now().strftime("%Y-%m-%d_%H_%M_%S") filename_01 = now + ".mp3" result = aipSpeech.synthesis( text_01,'zh',1,{'vol': 5,'per' : 2} ) if not isinstance(result, dict): with open(filename_01, 'wb') as f: f.write(result) print("--------------------------------------") time.sleep(1) pygame.mixer.init() print("语音1") file= filename_01 track = pygame.mixer.music.load(file) pygame.mixer.music.play() time.sleep(15) pygame.mixer.music.stop() pygame.quit()
新闻热点
疑难解答