前言
如同艺术家们用绘画让人们更贴切的感知世界,数据可视化也能让人们更直观的传递数据所要表达的信息。
我们今天就分享一下如何用 Python 简单便捷的完成数据可视化。
其实利用 Python 可视化数据并不是很麻烦,因为 Python 中有两个专用于可视化的库 matplotlib 和 seaborn 能让我们很容易的完成任务。
Matplotlib:基于Python的绘图库,提供完全的 2D 支持和部分 3D 图像支持。在跨平台和互动式环境中生成高质量数据时,matplotlib 会很有帮助。也可以用作制作动画。 Seaborn:该 Python 库能够创建富含信息量和美观的统计图形。Seaborn 基于 matplotlib,具有多种特性,比如内置主题、调色板、可以可视化单变量数据、双变量数据,线性回归数据和数据矩阵以及统计型时序数据等,能让我们创建复杂的可视化图形。我们用 Python 可以做出哪些可视化图形?
那么这里可能有人就要问了,我们为什么要做数据可视化?比如有下面这个图表:
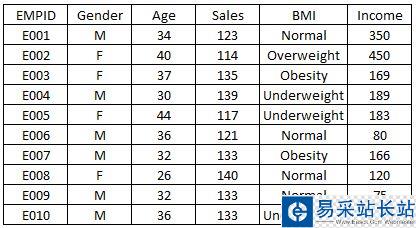
当然如果你把这张图表丢给别人,他们倒是也能看懂,但无法很直观的理解其中的信息,而且这种形式的图表看上去也比较 low,这个时候我们如果换成直观又美观的可视化图形,不仅能突显逼格,也能让人更容易的看懂数据。
下面我们就用上面这个简单的数据集作为例子,展示用 Python 做出9种可视化效果,并附有相关代码。
导入数据集
import matplotlib.pyplot as pltimport pandas as pddf=pd.read_excel("E:/First.xlsx", "Sheet1")可视化为直方图
fig=plt.figure() #Plots in matplotlib reside within a figure object, use plt.figure to create new figure#Create one or more subplots using add_subplot, because you can't create blank figureax = fig.add_subplot(1,1,1)#Variableax.hist(df['Age'],bins = 7) # Here you can play with number of binsLabels and Titplt.title('Age distribution')plt.xlabel('Age')plt.ylabel('#Employee')plt.show()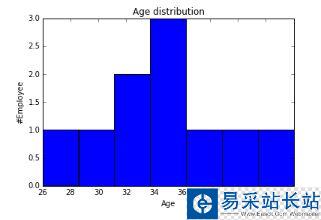
可视化为箱线图
import matplotlib.pyplot as pltimport pandas as pdfig=plt.figure()ax = fig.add_subplot(1,1,1)#Variableax.boxplot(df['Age'])plt.show()
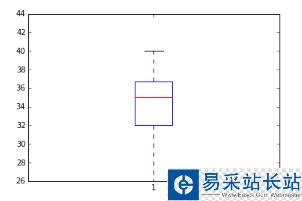
可视化为小提琴图
import seaborn as sns sns.violinplot(df['Age'], df['Gender']) #Variable Plotsns.despine()

可视化为条形图
var = df.groupby('Gender').Sales.sum() #grouped sum of sales at Gender levelfig = plt.figure()ax1 = fig.add_subplot(1,1,1)ax1.set_xlabel('Gender')ax1.set_ylabel('Sum of Sales')ax1.set_title("Gender wise Sum of Sales")var.plot(kind='bar')
新闻热点
疑难解答