本文实例讲述了Python定义二叉树及4种遍历方法。分享给大家供大家参考,具体如下:
二叉树是有限个元素的集合,该集合或者为空、或者有一个称为根节点(root)的元素及两个互不相交的、分别被称为左子树和右子树的二叉树组成。
二叉树的每个结点至多只有二棵子树(不存在度大于2的结点),二叉树的子树有左右之分,次序不能颠倒。 二叉树的第i层至多有2^{i-1}个结点 深度为k的二叉树至多有2^k-1个结点; 对任何一棵二叉树T,如果其终端结点数为N0,度为2的结点数为N2,则N0=N2+1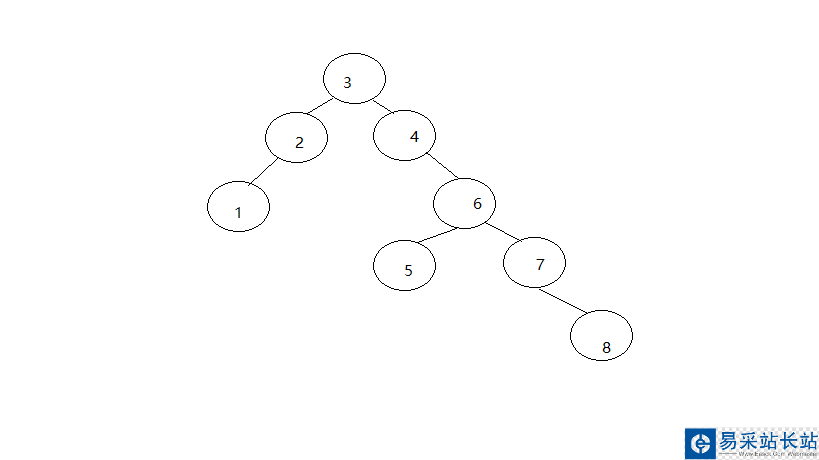
# init a treedef InitBinaryTree(dataSource, length): root = BTNode(dataSource[0]) for x in xrange(1,length): node = BTNode(dataSource[x]) InsertElementBinaryTree(root, node) return root print 'Done...'
# pre-orderdef PreorderTraversalBinaryTree(root): if root: print '%d | ' % root.data, PreorderTraversalBinaryTree(root.leftChild) PreorderTraversalBinaryTree(root.rightChild)
# in-orderdef InorderTraversalBinaryTree(root): if root: InorderTraversalBinaryTree(root.leftChild) print '%d | ' % root.data, InorderTraversalBinaryTree(root.rightChild)
# post-orderdef PostorderTraversalBinaryTree(root): if root: PostorderTraversalBinaryTree(root.leftChild) PostorderTraversalBinaryTree(root.rightChild) print '%d | ' % root.data,
# layer-orderdef TraversalByLayer(root, length): stack = [] stack.append(root) for x in xrange(length): node = stack[x] print '%d | ' % node.data, if node.leftChild: stack.append(node.leftChild) if node.rightChild: stack.append(node.rightChild)
Result

二叉树的思想重在“递归”, 并不是非要用递归处理,而是去理解二叉树递归的思想
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-#################### implement Binary Tree using python### Hongwing### 2016-9-4#################import mathclass BTNode(object): """docstring for BTNode""" def __init__(self, data): self.data = data self.leftChild = None self.rightChild = None# insert elementdef InsertElementBinaryTree(root, node): if root: if node.data < root.data: if root.leftChild: InsertElementBinaryTree(root.leftChild, node) else: root.leftChild = node else: if root.rightChild: InsertElementBinaryTree(root.rightChild, node) else: root.rightChild = node else: return 0# init a treedef InitBinaryTree(dataSource, length): root = BTNode(dataSource[0]) for x in xrange(1,length): node = BTNode(dataSource[x]) InsertElementBinaryTree(root, node) return root print 'Done...'# pre-orderdef PreorderTraversalBinaryTree(root): if root: print '%d | ' % root.data, PreorderTraversalBinaryTree(root.leftChild) PreorderTraversalBinaryTree(root.rightChild)# in-orderdef InorderTraversalBinaryTree(root): if root: InorderTraversalBinaryTree(root.leftChild) print '%d | ' % root.data, InorderTraversalBinaryTree(root.rightChild)# post-orderdef PostorderTraversalBinaryTree(root): if root: PostorderTraversalBinaryTree(root.leftChild) PostorderTraversalBinaryTree(root.rightChild) print '%d | ' % root.data,# layer-orderdef TraversalByLayer(root, length): stack = [] stack.append(root) for x in xrange(length): node = stack[x] print '%d | ' % node.data, if node.leftChild: stack.append(node.leftChild) if node.rightChild: stack.append(node.rightChild)if __name__ == '__main__': dataSource = [3, 4, 2, 6, 7, 1, 8, 5] length = len(dataSource) BTree = InitBinaryTree(dataSource, length) print '****NLR:' PreorderTraversalBinaryTree(BTree) print '/n****LNR' InorderTraversalBinaryTree(BTree) print '/n****LRN' PostorderTraversalBinaryTree(BTree) print '/n****LayerTraversal' TraversalByLayer(BTree, length)
新闻热点
疑难解答