1、文件常用操作汇总
2、打开文件
3、操作文件
4、关闭文件
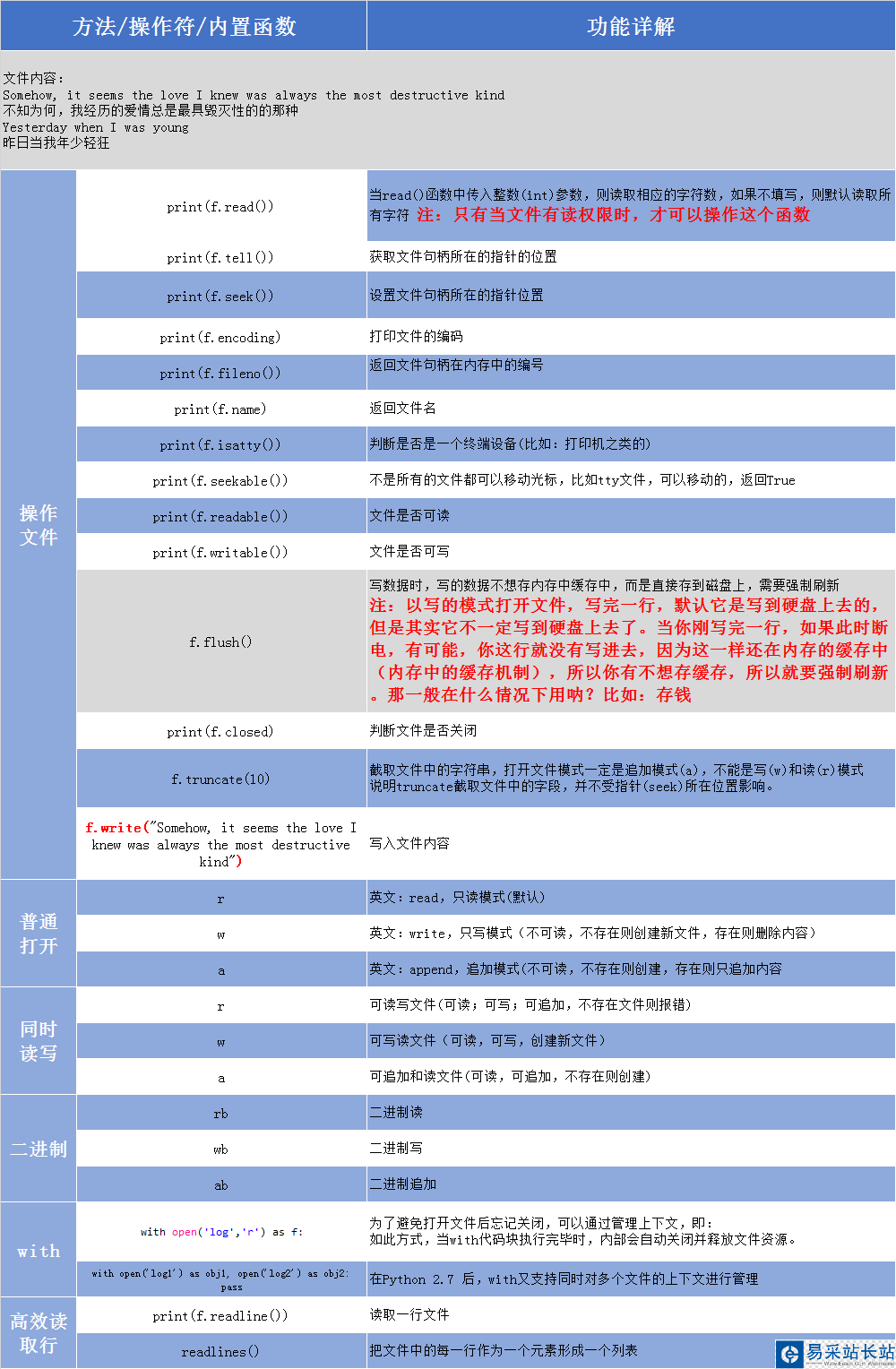
文件内容:
Somehow, it seems the love I knew was always the most destructive kind不知为何,我经历的爱情总是最具毁灭性的的那种Yesterday when I was young昨日当我年少轻狂
当read()函数中传入整数(int)参数,则读取相应的字符数,如果不填写,则默认读取所有字符
f = open("yesterday2",'r',encoding="utf-8")#默认读取全部字符print(f.read())f.close()#输出Somehow, it seems the love I knew was always the most destructive kind不知为何,我经历的爱情总是最具毁灭性的的那种Yesterday when I was young昨日当我年少轻狂 f = open("yesterday2",'r',encoding="utf-8")#只读取10个字符print(f.read(10))f.close()#输出Somehow, i注:只有当文件有读权限时,才可以操作这个函数
获取文件句柄所在的指针的位置
f = open("yesterday2",'r',encoding="utf-8")print(f.read(10))#获取指针位置print(f.tell())f.close()#输出Somehow, i #读取的内容10 #指针位置f = open("yesterday2",'r',encoding="utf-8")print(f.read(10))#设置之前的指针位置print(f.tell())f.seek(0)#设置之后的指针位置print(f.tell())f.close()#输出Somehow, i #读取文件的内容10 #设置之前的指针位置0 #设置之后的指针位置f = open("yesterday2",'r',encoding="utf-8")print(f.encoding)f.close()#输出utf-8返回文件句柄在内存中的编号
f = open("yesterday2",'r',encoding="utf-8")print(f.fileno())f.close()#输出3返回文件名
f = open("yesterday2",'r',encoding="utf-8")print(f.name)f.close()#输出yesterday2判断是否是一个终端设备(比如:打印机之类的)
新闻热点
疑难解答