python实现简单神经网络算法,供大家参考,具体内容如下
python实现二层神经网络
包括输入层和输出层
import numpy as np #sigmoid function def nonlin(x, deriv = False): if(deriv == True): return x*(1-x) return 1/(1+np.exp(-x)) #input dataset x = np.array([[0,0,1], [0,1,1], [1,0,1], [1,1,1]]) #output dataset y = np.array([[0,0,1,1]]).T np.random.seed(1) #init weight value syn0 = 2*np.random.random((3,1))-1 for iter in xrange(100000): l0 = x #the first layer,and the input layer l1 = nonlin(np.dot(l0,syn0)) #the second layer,and the output layer l1_error = y-l1 l1_delta = l1_error*nonlin(l1,True) syn0 += np.dot(l0.T, l1_delta) print "outout after Training:" print l1
import numpy as np #sigmoid function def nonlin(x, deriv = False): if(deriv == True): return x*(1-x) return 1/(1+np.exp(-x)) #input dataset x = np.array([[0,0,1], [0,1,1], [1,0,1], [1,1,1]]) #output dataset y = np.array([[0,0,1,1]]).T np.random.seed(1) #init weight value syn0 = 2*np.random.random((3,1))-1 for iter in xrange(100000): l0 = x #the first layer,and the input layer l1 = nonlin(np.dot(l0,syn0)) #the second layer,and the output layer l1_error = y-l1 l1_delta = l1_error*nonlin(l1,True) syn0 += np.dot(l0.T, l1_delta) print "outout after Training:" print l1
这里,
l0:输入层
l1:输出层
syn0:初始权值
l1_error:误差
l1_delta:误差校正系数
func nonlin:sigmoid函数
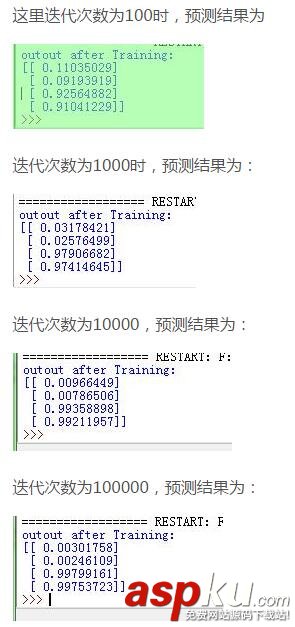
可见迭代次数越多,预测结果越接近理想值,当时耗时也越长。
python实现三层神经网络
包括输入层、隐含层和输出层
import numpy as np def nonlin(x, deriv = False): if(deriv == True): return x*(1-x) else: return 1/(1+np.exp(-x)) #input dataset X = np.array([[0,0,1], [0,1,1], [1,0,1], [1,1,1]]) #output dataset y = np.array([[0,1,1,0]]).T syn0 = 2*np.random.random((3,4)) - 1 #the first-hidden layer weight value syn1 = 2*np.random.random((4,1)) - 1 #the hidden-output layer weight value for j in range(60000): l0 = X #the first layer,and the input layer l1 = nonlin(np.dot(l0,syn0)) #the second layer,and the hidden layer l2 = nonlin(np.dot(l1,syn1)) #the third layer,and the output layer l2_error = y-l2 #the hidden-output layer error if(j%10000) == 0: print "Error:"+str(np.mean(l2_error)) l2_delta = l2_error*nonlin(l2,deriv = True) l1_error = l2_delta.dot(syn1.T) #the first-hidden layer error l1_delta = l1_error*nonlin(l1,deriv = True) syn1 += l1.T.dot(l2_delta) syn0 += l0.T.dot(l1_delta) print "outout after Training:" print l2
import numpy as np def nonlin(x, deriv = False): if(deriv == True): return x*(1-x) else: return 1/(1+np.exp(-x)) #input dataset X = np.array([[0,0,1], [0,1,1], [1,0,1], [1,1,1]]) #output dataset y = np.array([[0,1,1,0]]).T syn0 = 2*np.random.random((3,4)) - 1 #the first-hidden layer weight value syn1 = 2*np.random.random((4,1)) - 1 #the hidden-output layer weight value for j in range(60000): l0 = X #the first layer,and the input layer l1 = nonlin(np.dot(l0,syn0)) #the second layer,and the hidden layer l2 = nonlin(np.dot(l1,syn1)) #the third layer,and the output layer l2_error = y-l2 #the hidden-output layer error if(j%10000) == 0: print "Error:"+str(np.mean(l2_error)) l2_delta = l2_error*nonlin(l2,deriv = True) l1_error = l2_delta.dot(syn1.T) #the first-hidden layer error l1_delta = l1_error*nonlin(l1,deriv = True) syn1 += l1.T.dot(l2_delta) syn0 += l0.T.dot(l1_delta) print "outout after Training:" print l2
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持VEVB武林网。
新闻热点
疑难解答