本文将实现逻辑回归算法,预测低出生体重的概率。
# Logistic Regression# 逻辑回归#----------------------------------## This function shows how to use TensorFlow to# solve logistic regression.# y = sigmoid(Ax + b)## We will use the low birth weight data, specifically:# y = 0 or 1 = low birth weight# x = demographic and medical history dataimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltimport numpy as npimport tensorflow as tfimport requestsfrom tensorflow.python.framework import opsimport os.pathimport csvops.reset_default_graph()# Create graphsess = tf.Session()#### Obtain and prepare data for modeling#### name of data filebirth_weight_file = 'birth_weight.csv'# download data and create data file if file does not exist in current directoryif not os.path.exists(birth_weight_file): birthdata_url = 'https://github.com/nfmcclure/tensorflow_cookbook/raw/master/01_Introduction/07_Working_with_Data_Sources/birthweight_data/birthweight.dat' birth_file = requests.get(birthdata_url) birth_data = birth_file.text.split('/r/n') birth_header = birth_data[0].split('/t') birth_data = [[float(x) for x in y.split('/t') if len(x)>=1] for y in birth_data[1:] if len(y)>=1] with open(birth_weight_file, "w") as f: writer = csv.writer(f) writer.writerow(birth_header) writer.writerows(birth_data) f.close()# read birth weight data into memorybirth_data = []with open(birth_weight_file, newline='') as csvfile: csv_reader = csv.reader(csvfile) birth_header = next(csv_reader) for row in csv_reader: birth_data.append(row)birth_data = [[float(x) for x in row] for row in birth_data]# Pull out target variabley_vals = np.array([x[0] for x in birth_data])# Pull out predictor variables (not id, not target, and not birthweight)x_vals = np.array([x[1:8] for x in birth_data])# set for reproducible resultsseed = 99np.random.seed(seed)tf.set_random_seed(seed)# Split data into train/test = 80%/20%# 分割数据集为测试集和训练集train_indices = np.random.choice(len(x_vals), round(len(x_vals)*0.8), replace=False)test_indices = np.array(list(set(range(len(x_vals))) - set(train_indices)))x_vals_train = x_vals[train_indices]x_vals_test = x_vals[test_indices]y_vals_train = y_vals[train_indices]y_vals_test = y_vals[test_indices]# Normalize by column (min-max norm)# 将所有特征缩放到0和1区间(min-max缩放),逻辑回归收敛的效果更好# 归一化特征def normalize_cols(m): col_max = m.max(axis=0) col_min = m.min(axis=0) return (m-col_min) / (col_max - col_min)x_vals_train = np.nan_to_num(normalize_cols(x_vals_train))x_vals_test = np.nan_to_num(normalize_cols(x_vals_test))#### Define Tensorflow computational graph¶#### Declare batch sizebatch_size = 25# Initialize placeholdersx_data = tf.placeholder(shape=[None, 7], dtype=tf.float32)y_target = tf.placeholder(shape=[None, 1], dtype=tf.float32)# Create variables for linear regressionA = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal(shape=[7,1]))b = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal(shape=[1,1]))# Declare model operationsmodel_output = tf.add(tf.matmul(x_data, A), b)# Declare loss function (Cross Entropy loss)loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=model_output, labels=y_target))# Declare optimizermy_opt = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.01)train_step = my_opt.minimize(loss)#### Train model#### Initialize variablesinit = tf.global_variables_initializer()sess.run(init)# Actual Prediction# 除记录损失函数外,也需要记录分类器在训练集和测试集上的准确度。# 所以创建一个返回准确度的预测函数prediction = tf.round(tf.sigmoid(model_output))predictions_correct = tf.cast(tf.equal(prediction, y_target), tf.float32)accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(predictions_correct)# Training loop# 开始遍历迭代训练,记录损失值和准确度loss_vec = []train_acc = []test_acc = []for i in range(1500): rand_index = np.random.choice(len(x_vals_train), size=batch_size) rand_x = x_vals_train[rand_index] rand_y = np.transpose([y_vals_train[rand_index]]) sess.run(train_step, feed_dict={x_data: rand_x, y_target: rand_y}) temp_loss = sess.run(loss, feed_dict={x_data: rand_x, y_target: rand_y}) loss_vec.append(temp_loss) temp_acc_train = sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict={x_data: x_vals_train, y_target: np.transpose([y_vals_train])}) train_acc.append(temp_acc_train) temp_acc_test = sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict={x_data: x_vals_test, y_target: np.transpose([y_vals_test])}) test_acc.append(temp_acc_test) if (i+1)%300==0: print('Loss = ' + str(temp_loss))#### Display model performance#### 绘制损失和准确度plt.plot(loss_vec, 'k-')plt.title('Cross Entropy Loss per Generation')plt.xlabel('Generation')plt.ylabel('Cross Entropy Loss')plt.show()# Plot train and test accuracyplt.plot(train_acc, 'k-', label='Train Set Accuracy')plt.plot(test_acc, 'r--', label='Test Set Accuracy')plt.title('Train and Test Accuracy')plt.xlabel('Generation')plt.ylabel('Accuracy')plt.legend(loc='lower right')plt.show()
数据结果:
Loss = 0.845124
Loss = 0.658061
Loss = 0.471852
Loss = 0.643469
Loss = 0.672077
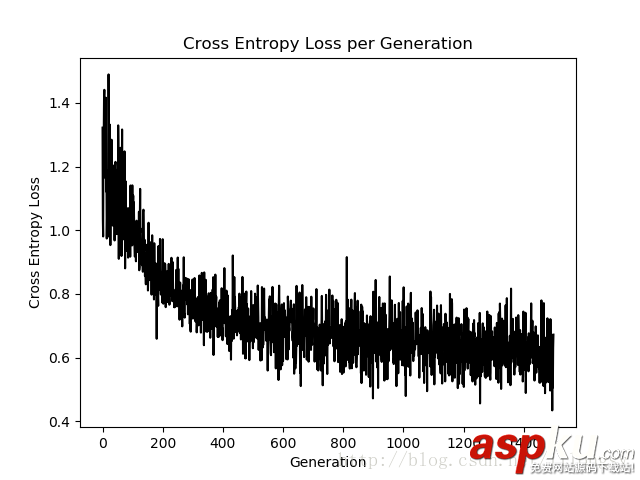
迭代1500次的交叉熵损失图
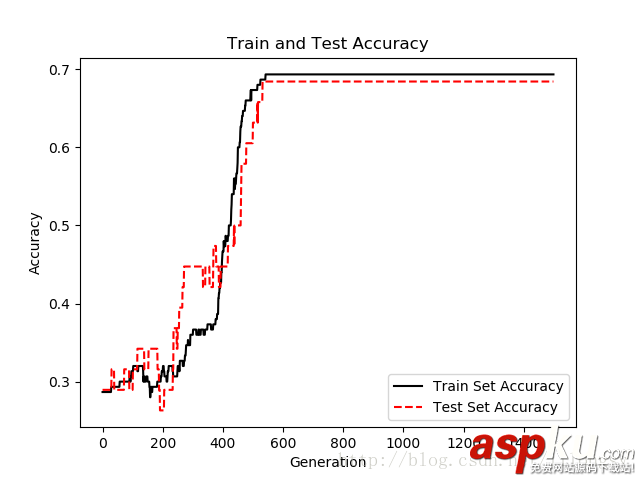
迭代1500次的测试集和训练集的准确度图
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持VEVB武林网。
新闻热点
疑难解答