如果最小二乘线性回归算法最小化到回归直线的竖直距离(即,平行于y轴方向),则戴明回归最小化到回归直线的总距离(即,垂直于回归直线)。其最小化x值和y值两个方向的误差,具体的对比图如下图。

线性回归算法和戴明回归算法的区别。左边的线性回归最小化到回归直线的竖直距离;右边的戴明回归最小化到回归直线的总距离。
线性回归算法的损失函数最小化竖直距离;而这里需要最小化总距离。给定直线的斜率和截距,则求解一个点到直线的垂直距离有已知的几何公式。代入几何公式并使TensorFlow最小化距离。
损失函数是由分子和分母组成的几何公式。给定直线y=mx+b,点(x0,y0),则求两者间的距离的公式为:
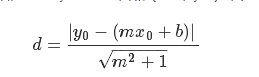
# 戴明回归#----------------------------------## This function shows how to use TensorFlow to# solve linear Deming regression.# y = Ax + b## We will use the iris data, specifically:# y = Sepal Length# x = Petal Widthimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltimport numpy as npimport tensorflow as tffrom sklearn import datasetsfrom tensorflow.python.framework import opsops.reset_default_graph()# Create graphsess = tf.Session()# Load the data# iris.data = [(Sepal Length, Sepal Width, Petal Length, Petal Width)]iris = datasets.load_iris()x_vals = np.array([x[3] for x in iris.data])y_vals = np.array([y[0] for y in iris.data])# Declare batch sizebatch_size = 50# Initialize placeholdersx_data = tf.placeholder(shape=[None, 1], dtype=tf.float32)y_target = tf.placeholder(shape=[None, 1], dtype=tf.float32)# Create variables for linear regressionA = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal(shape=[1,1]))b = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal(shape=[1,1]))# Declare model operationsmodel_output = tf.add(tf.matmul(x_data, A), b)# Declare Demming loss functiondemming_numerator = tf.abs(tf.subtract(y_target, tf.add(tf.matmul(x_data, A), b)))demming_denominator = tf.sqrt(tf.add(tf.square(A),1))loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.truediv(demming_numerator, demming_denominator))# Declare optimizermy_opt = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.1)train_step = my_opt.minimize(loss)# Initialize variablesinit = tf.global_variables_initializer()sess.run(init)# Training looploss_vec = []for i in range(250): rand_index = np.random.choice(len(x_vals), size=batch_size) rand_x = np.transpose([x_vals[rand_index]]) rand_y = np.transpose([y_vals[rand_index]]) sess.run(train_step, feed_dict={x_data: rand_x, y_target: rand_y}) temp_loss = sess.run(loss, feed_dict={x_data: rand_x, y_target: rand_y}) loss_vec.append(temp_loss) if (i+1)%50==0: print('Step #' + str(i+1) + ' A = ' + str(sess.run(A)) + ' b = ' + str(sess.run(b))) print('Loss = ' + str(temp_loss))# Get the optimal coefficients[slope] = sess.run(A)[y_intercept] = sess.run(b)# Get best fit linebest_fit = []for i in x_vals: best_fit.append(slope*i+y_intercept)# Plot the resultplt.plot(x_vals, y_vals, 'o', label='Data Points')plt.plot(x_vals, best_fit, 'r-', label='Best fit line', linewidth=3)plt.legend(loc='upper left')plt.title('Sepal Length vs Pedal Width')plt.xlabel('Pedal Width')plt.ylabel('Sepal Length')plt.show()# Plot loss over timeplt.plot(loss_vec, 'k-')plt.title('L2 Loss per Generation')plt.xlabel('Generation')plt.ylabel('L2 Loss')plt.show()结果:


本文的戴明回归算法与线性回归算法得到的结果基本一致。两者之间的关键不同点在于预测值与数据点间的损失函数度量:线性回归算法的损失函数是竖直距离损失;而戴明回归算法是垂直距离损失(到x轴和y轴的总距离损失)。
注意,这里戴明回归算法的实现类型是总体回归(总的最小二乘法误差)。总体回归算法是假设x值和y值的误差是相似的。我们也可以根据不同的理念使用不同的误差来扩展x轴和y轴的距离计算。
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持VEVB武林网。
新闻热点
疑难解答