编译原理老师要求写一个java的词法分析器,想了想决定用python写一个。
目标
能识别出变量,数字,运算符,界符和关键字,用excel表打印出来。
有了目标,想想要怎么实现词法分析器。
1.先进行预处理,把注释,多余的空格,空行去掉。
2.一行一行扫描,行里逐字扫描,把界符和运算符当做分割符,遇到就先停下开始判断。
- 若是以 英文字母、$、下划线开头,则可能是变量和关键字,在判断是关键字还是变量。
- 若是数字开头,则判断下一位是不是也是数字,直到遇到非数字停止,在把数字取出来。
- 再来判断分割符是什么类型,是界符还是运算符。
在给不同词添加上识别码
在用excel表打印出来。
代码实现
1. 用列表创建一个关键字表,java关键字有50个。
#保留字key_word = ['abstract','assert','boolean','break','byte', 'case','catch','char','class','const', 'continue','default','do','double','else', 'enum','extends','final','finally','float', 'for','goto','if','implements','import', 'instanceof','int','interface','long','native', 'new','package','private','protected','public', 'return','short','static','strictfp','super', 'switch','synchronized','this','throw','throws', 'transient','try','void','volatile','while']
2.用列表创建一个运算符表。
#运算符operator = ['+','-','*','/','%','++','--','+=','-=','+=','/=',#算术运算符 '==','!=','>','<','>=','<=',#关系运算符 '&','|','^','~','<<','>>','>>>',#位运算符 '&&','||','!',#逻辑运算符 '=','+=','-=','*=','/=','%=','<<=','>>=','&=','^=','|=',#赋值运算符 '?:']#条件运算符
3. 用列表创建一个界符表。
#界符delimiters = ['{','}','[',']','(',')','.',',',':',';'] 4.预处理
用正则表达式把注释去掉,在把多余的空行去掉
#预处理def filterResource(file,new_file): f2 = open(new_file,'w+') txt = ''.join(open(file,'r').readlines()) deal_txt = re.sub(r'///*[/s/S]*/*//|////.*','',txt) for line in deal_txt.split('/n'): line = line.strip() line = line.replace('//t','') line = line.replace('//n','') if not line: continue else: f2.write(line+'/n') f2.close() return sys.path[0]+'//'+ new_file 5.逐行扫描
按照刚刚的思路进行判断,把每一行的单词,添加到word_line列表中,最后在把每一行添加到token列表中。
def Scan(file): lines = open(file,'r').readlines() for line in lines: word = '' word_line = [] i = 0 while i <len(line): word +=line[i] if line[i]==' ' or line[i] in delimiters or line[i] in operator: if word[0].isalpha() or word[0]=='$' or word[0]=='_': word = word[:-1] if searchReserve(word): # 保留字 word_line.append({word[:-1]:key_word.index(word)}) else: # 标识符 identifier.append({word:-2}) word_line.append({word:-2}) # 常数 elif word[:-1].isdigit(): word_line.append({word:-1}) #else: #error_word.append(word) # 字符是界符 if line[i] in delimiters: word_line.append({line[i]:len(key_word)+delimiters.index(line[i])}) # 字符是运算符 elif line[i] in operator: s = line[i] +line[i+1] if s in operator: word_line.append({s:len(key_word)+len(delimiters)+operator.index(s)}) i +=1 else: word_line.append({line[i]:len(key_word)+len(delimiters)+operator.index(line[i])}) word = '' i+=1 token.append(word_line) 6.根据单词返回是什么类型
按照保留字--界符--运算符--常数的顺序来当识别码。常数识别码是-1,标识符识别码是-2
def check(number): hanzi = '' q = len(key_word) w = len(delimiters) e = len(operator) if 0<number<=q: hanzi = '保留字' elif q<number <= q+w: hanzi = '界符' elif q+w<number <=q+w+e: hanzi = '运算符' elif number == -1: hanzi ='常数' elif number == -2: hanzi ='标识符' return hanzi
7. 用thinker写一个简单的界面
导入
from tkinter import * from tkinter.filedialog import askdirectory,askopenfilename
root = Tk() root.title('词法分析') root.resizable(0, 0) path = StringVar() Label(root,text = "目标路径:").grid(row = 0, column = 0) Entry(root, textvariable = path).grid(row = 0, column = 1) Button(root, text = "路径选择", command = openfiles).grid(row = 0, column = 2) Button(root,text='词法分析',command= open_excel).grid(row = 0,column = 3) root.mainloop() 打开文件
def openfiles(): fname = askopenfilename(title='打开文件', filetypes=[('All Files', '*')]) path.set(fname) 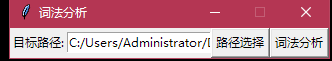
简单的界面
8.导入到excel表中
需要安装包xwings
导入
把token里的单词,按照 单词 ---- 识别码 ---类型 打印到excel表中
def open_excel(): # 预处理 row,col=0,0 if path.get()!='': txt = java_analysis.filterResource(path.get(),new_file) print(txt) #扫描 java_analysis.Scan(txt) app = xw.App(visible=True,add_book=False) wb =app.books.open(sys.path[0]+'//'+'test.xlsx') sheet = wb.sheets.active sheet.clear() print(java_analysis.token) for i in range(len(java_analysis.token)): sheet[row,0].value = '第'+str(i+1)+'行' row +=1 for word in java_analysis.token[i]: for k,w in word.items(): sheet[row,3].value = k sheet[row,5].value = w sheet[row,7].value = java_analysis.check(w) row +=1 sheet.autofit()#整个sheet自动调整 #wb.save()
最后就像这样
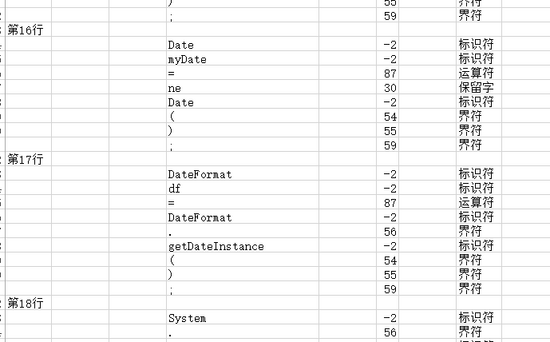
效果
代码很烂,不过也算是大致明白词法分析器了。
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持VEVB武林网。
注:相关教程知识阅读请移步到python教程频道。