我们都知道support库有一个DividerItemDecoration, 可以作为Item之间的分隔线(divider)。但它作用以后所有的item之间都会有这个分隔线,实际情况往往是:recyclerView中存在多种的视图类型(viewType), 我们只是需要在某一类型的视图后添加分隔线。
要实现这种分隔线效果并不是什么难事,既然是某一类型有这个分隔线,那在直接在这种视图的layout文件上增加如下一个bottomLine界面元素妥妥的:
<View android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="0.5dp" android:background="@color/colorGrayLight" />
但如果添加这样一个界面元素导致新增一层布局那感觉代价有点大。另外一种情况,如果当前这个视图由于某种原因存在padding,而期望的分隔线是穿透整个布局的,那添加bottomLine的做法也是行不通的;还有一种情况同一类型布局在一个页面有分隔线,在另一个页面没有分隔线;总之就是希望分隔线和视图内容无关。所以我们需要一种类似DividerItemDecoration的decoration,它能针对某些viewType起作用。
先要了解一下RecyclerView.ItemDecoration,它有2个重要的回调方法:onDrawOver和getItemOffsets。onDrawOver其实是一种应用多个item的方法,所以无论如何都需要一个遍历操作。需要理解的是getItemOffsets中outRect这个输出型参数,虽然是一个Rect类型,但并不表示任何范围,而只是一个item四周的间隔距离:
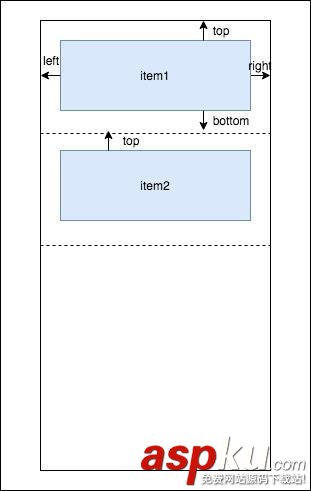
outRect参数各域的含义
我们思路已经很清楚了: 在getItemOffsets中判断当前view的类型(parent.getChildViewHolder(view)), 如果是我们需要的类型设置对应的bottom;在onDrawOver中我们遍历recyclerView的child,同样如果是我们需要的类型将分隔线画在对应位置上就行了;这个decoration可以针对任意一种或者几种类型设置不种的drawable,我们当前用SparseArray存储,key就是视图的viewType
private final SparseArrayCompat<Drawable> mDividers = new SparseArrayCompat<>(2);
同时我们可以设置这个item的高度,当Drawable为null时相当于一个透明的间隙,不为null时具有强制指定的高度。
同样我们还要考虑方向:layoutManager为横向和竖向的情况,无它,只是画的位置不同而已。
话不多说了,上代码:
import android.graphics.drawable.Drawable;import android.support.annotation.Nullable;import android.support.v7.widget.RecyclerView;public class ViewTypeDivider extends ItemHolderDivider { @Override protected int keyFrom(RecyclerView.ViewHolder holder) { return holder.getItemViewType(); } public ViewTypeDivider put(int viewType, Drawable drawable) { putDrawable(viewType, drawable); return this; } public ViewTypeDivider put(int viewType, @Nullable Drawable drawable, int height) { putHeight(viewType, drawable, height); return this; }}import android.graphics.Canvas;import android.graphics.Rect;import android.graphics.drawable.Drawable;import android.support.annotation.Nullable;import android.support.v4.util.SparseArrayCompat;import android.support.v7.widget.LinearLayoutManager;import android.support.v7.widget.RecyclerView;import android.view.View;abstract class ItemHolderDivider extends RecyclerView.ItemDecoration { private final SparseArrayCompat<Drawable> mDividers = new SparseArrayCompat<>(2); private final SparseArrayCompat<Integer> mHeights = new SparseArrayCompat<>(2); protected abstract int keyFrom(RecyclerView.ViewHolder holder); @Override public void onDrawOver(Canvas c, RecyclerView parent, RecyclerView.State state) { final int childCount = parent.getChildCount(); final int width = parent.getWidth(); final int height = parent.getHeight(); for (int childViewIndex = 0; childViewIndex < childCount; childViewIndex++) { final View view = parent.getChildAt(childViewIndex); RecyclerView.ViewHolder holder = parent.getChildViewHolder(view); int key = keyFrom(holder); if (isVertical(parent)) { drawBottom(c, key, (int) view.getY() + view.getHeight(), width); drawTop(c, -key, (int) view.getY(), width); } else { drawRight(c, key, (int) view.getX() + view.getWidth(), height); drawLeft(c, -key, (int) view.getX(), height); } } } @Override public void getItemOffsets(Rect outRect, View view, RecyclerView parent, RecyclerView.State state) { RecyclerView.ViewHolder holder = parent.getChildViewHolder(view); int key = keyFrom(holder); if (isVertical(parent)) { outRect.bottom = getHeight(key); outRect.top = getHeight(-key); } else { outRect.right = getHeight(key); outRect.left = getHeight(-key); } } private void drawBottom(Canvas c, int key, int y, int width) { Drawable d = mDividers.get(key); if (d != null) { d.setBounds(0, y, width, y + getHeight(key, d)); d.draw(c); } } private void drawTop(Canvas c, int key, int y, int width) { Drawable d = mDividers.get(key); if (d != null) { d.setBounds(0, y - getHeight(key, d), width, y); d.draw(c); } } private void drawRight(Canvas c, int key, int x, int height) { Drawable d = mDividers.get(key); if (d != null) { d.setBounds(x, 0, x + getHeight(key, d), height); d.draw(c); } } private void drawLeft(Canvas c, int key, int x, int height) { Drawable d = mDividers.get(key); if (d != null) { d.setBounds(x - getHeight(key, d), 0, x, height); d.draw(c); } } final void putDrawable(int key, Drawable drawable) { mDividers.put(key, drawable); } final void putHeight(int key, @Nullable Drawable drawable, int height) { if (drawable != null) { mDividers.put(key, drawable); } mHeights.put(key, height); } private int getHeight(int key) { Drawable d = mDividers.get(key); return getHeight(key, d); } private int getHeight(int key, @Nullable Drawable d) { int index = mHeights.indexOfKey(key); return index < 0 ? d == null ? 0 : d.getIntrinsicHeight() : mHeights.valueAt(index); } private boolean isVertical(RecyclerView parent) { RecyclerView.LayoutManager layoutManager = parent.getLayoutManager(); return !(layoutManager instanceof LinearLayoutManager) || ((LinearLayoutManager) layoutManager).getOrientation() == LinearLayoutManager.VERTICAL; }}以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持VEVB武林网。
新闻热点
疑难解答