1. invalidate 和 postInvalidate 的关系
postInvalidate 是通过 Handler 切换回到主线程,然后在调用 invalidate 的,源码:
public void postInvalidate() { postInvalidateDelayed(0); } public void postInvalidateDelayed(long delayMilliseconds) { // We try only with the AttachInfo because there's no point in invalidating // if we are not attached to our window final AttachInfo attachInfo = mAttachInfo; if (attachInfo != null) { attachInfo.mViewRootImpl.dispatchInvalidateDelayed(this, delayMilliseconds); } } // ViewRootImpl 中 public void dispatchInvalidateDelayed(View view, long delayMilliseconds) { Message msg = mHandler.obtainMessage(MSG_INVALIDATE, view); mHandler.sendMessageDelayed(msg, delayMilliseconds); } final class ViewRootHandler extends Handler { @Override public void handleMessage(Message msg) { switch (msg.what) { case MSG_INVALIDATE: ((View) msg.obj).invalidate(); break; ... }2. 子线程是否可以更新 UI ?
可以的,在 Activity 的 onCreate 中直接开启子线程并在子线程中更新 UI 是没问题的:
public class MainActivity extends Activity { private TextView tvText; @Override public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); tvText = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.main_tv); new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { try { Thread.sleep(200); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } tvText.setText("OtherThread"); } }).start(); }}原因:校验线程是 ViewRootImpl 来做的,但是它的创建流程是在 Activity 的 onResume 的时候:
// ActivityThread 中 final void handleResumeActivity(IBinder token, boolean clearHide, boolean isForward, boolean reallyResume, int seq, String reason) { ActivityClientRecord r = mActivities.get(token); ... if (r != null) { final Activity a = r.activity; if (r.window == null && !a.mFinished && willBeVisible) { r.window = r.activity.getWindow(); View decor = r.window.getDecorView(); decor.setVisibility(View.INVISIBLE); ViewManager wm = a.getWindowManager(); WindowManager.LayoutParams l = r.window.getAttributes(); ... if (a.mVisibleFromClient) { if (!a.mWindowAdded) { a.mWindowAdded = true; // 关键代码 wm.addView(decor, l); } else { a.onWindowAttributesChanged(l); } } ... } // WindowManagerGlobal 中 public void addView(View view, ViewGroup.LayoutParams params, Display display, Window parentWindow) { ... ViewRootImpl root; View panelParentView = null; synchronized (mLock) { ... // 在这里创建 ViewRootImpl root = new ViewRootImpl(view.getContext(), display); view.setLayoutParams(wparams); ... } } // 在 ViewRootImpl 中有这么段代码,所有更新 UI 都会走到这里 void checkThread() { if (mThread != Thread.currentThread()) { // mThread 就是主线程 throw new CalledFromWrongThreadException( "Only the original thread that created a view hierarchy can touch its views."); } }所以子线程只要在 ViewRootImpl 创建之前更新 UI 就没问题!
3. invalidate 的源码分析
先看一张图:
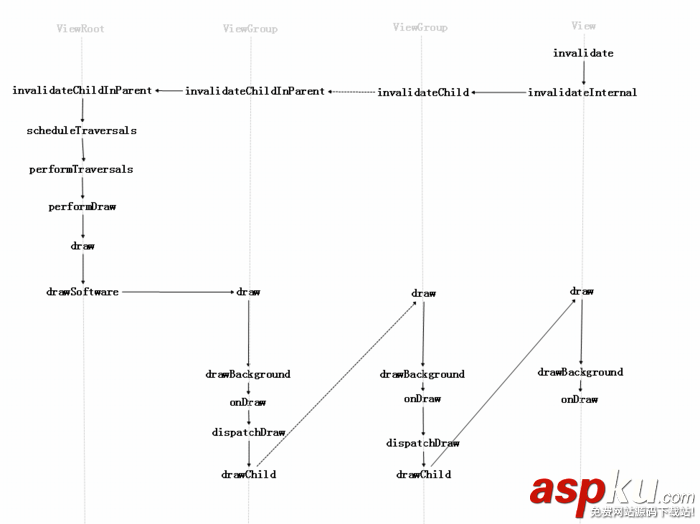
invalidate 的流程
于是自己尝试走走源码:
// view 中 public void invalidate() { invalidate(true); } public void invalidate(boolean invalidateCache) { invalidateInternal(0, 0, mRight - mLeft, mBottom - mTop, invalidateCache, true); } void invalidateInternal(int l, int t, int r, int b, boolean invalidateCache, boolean fullInvalidate) { if (mGhostView != null) { mGhostView.invalidate(true); return; } if (skipInvalidate()) { return; } if ((mPrivateFlags & (PFLAG_DRAWN | PFLAG_HAS_BOUNDS)) == (PFLAG_DRAWN | PFLAG_HAS_BOUNDS) || (invalidateCache && (mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_DRAWING_CACHE_VALID) == PFLAG_DRAWING_CACHE_VALID) || (mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_INVALIDATED) != PFLAG_INVALIDATED || (fullInvalidate && isOpaque() != mLastIsOpaque)) { if (fullInvalidate) { mLastIsOpaque = isOpaque(); mPrivateFlags &= ~PFLAG_DRAWN; } mPrivateFlags |= PFLAG_DIRTY; if (invalidateCache) { mPrivateFlags |= PFLAG_INVALIDATED; mPrivateFlags &= ~PFLAG_DRAWING_CACHE_VALID; } // Propagate the damage rectangle to the parent view. final AttachInfo ai = mAttachInfo; final ViewParent p = mParent; if (p != null && ai != null && l < r && t < b) { final Rect damage = ai.mTmpInvalRect; damage.set(l, t, r, b); // 调用父类的 invalidateChild 方法 p.invalidateChild(this, damage); } // Damage the entire projection receiver, if necessary. if (mBackground != null && mBackground.isProjected()) { final View receiver = getProjectionReceiver(); if (receiver != null) { receiver.damageInParent(); } } } }看到 View 的 invalidate 最后是调用了 p.invalidateChild(this, damage); p 是 ViewParent 的对象,具体实现是 ViewGroup
// ViewGroup 中 @Override public final void invalidateChild(View child, final Rect dirty) { final AttachInfo attachInfo = mAttachInfo; ... ViewParent parent = this; do { View view = null; ... // 关键代码 parent = parent.invalidateChildInParent(location, dirty); ... } while (parent != null); } @Override public ViewParent invalidateChildInParent(final int[] location, final Rect dirty) { if ((mPrivateFlags & (PFLAG_DRAWN | PFLAG_DRAWING_CACHE_VALID)) != 0) { // either DRAWN, or DRAWING_CACHE_VALID if ((mGroupFlags & (FLAG_OPTIMIZE_INVALIDATE | FLAG_ANIMATION_DONE)) != FLAG_OPTIMIZE_INVALIDATE) { dirty.offset(location[CHILD_LEFT_INDEX] - mScrollX, location[CHILD_TOP_INDEX] - mScrollY); if ((mGroupFlags & FLAG_CLIP_CHILDREN) == 0) { dirty.union(0, 0, mRight - mLeft, mBottom - mTop); } final int left = mLeft; final int top = mTop; if ((mGroupFlags & FLAG_CLIP_CHILDREN) == FLAG_CLIP_CHILDREN) { if (!dirty.intersect(0, 0, mRight - left, mBottom - top)) { dirty.setEmpty(); } } location[CHILD_LEFT_INDEX] = left; location[CHILD_TOP_INDEX] = top; } else { if ((mGroupFlags & FLAG_CLIP_CHILDREN) == FLAG_CLIP_CHILDREN) { dirty.set(0, 0, mRight - mLeft, mBottom - mTop); } else { // in case the dirty rect extends outside the bounds of this container dirty.union(0, 0, mRight - mLeft, mBottom - mTop); } location[CHILD_LEFT_INDEX] = mLeft; location[CHILD_TOP_INDEX] = mTop; mPrivateFlags &= ~PFLAG_DRAWN; } mPrivateFlags &= ~PFLAG_DRAWING_CACHE_VALID; if (mLayerType != LAYER_TYPE_NONE) { mPrivateFlags |= PFLAG_INVALIDATED; } return mParent; } return null; }上面 invalidateChildInParent 开始时会调用 ViewGroup 自己的 invalidateChildInParent 方法,但到最后还是会调用到 ViewRootImpl 中的 invalidateChildInParent,看下 ViewRootImpl 中的具体实现
// ViewRootImpl 中 @Override public ViewParent invalidateChildInParent(int[] location, Rect dirty) { checkThread(); if (DEBUG_DRAW) Log.v(mTag, "Invalidate child: " + dirty); if (dirty == null) { invalidate(); return null; } else if (dirty.isEmpty() && !mIsAnimating) { return null; } if (mCurScrollY != 0 || mTranslator != null) { mTempRect.set(dirty); dirty = mTempRect; if (mCurScrollY != 0) { dirty.offset(0, -mCurScrollY); } if (mTranslator != null) { mTranslator.translateRectInAppWindowToScreen(dirty); } if (mAttachInfo.mScalingRequired) { dirty.inset(-1, -1); } } // 又调用了这个方法 invalidateRectOnScreen(dirty); return null; } private void invalidateRectOnScreen(Rect dirty) { final Rect localDirty = mDirty; if (!localDirty.isEmpty() && !localDirty.contains(dirty)) { mAttachInfo.mSetIgnoreDirtyState = true; mAttachInfo.mIgnoreDirtyState = true; } // Add the new dirty rect to the current one localDirty.union(dirty.left, dirty.top, dirty.right, dirty.bottom); // Intersect with the bounds of the window to skip // updates that lie outside of the visible region final float appScale = mAttachInfo.mApplicationScale; final boolean intersected = localDirty.intersect(0, 0, (int) (mWidth * appScale + 0.5f), (int) (mHeight * appScale + 0.5f)); if (!intersected) { localDirty.setEmpty(); } if (!mWillDrawSoon && (intersected || mIsAnimating)) { // 关键又调用了这个方法 scheduleTraversals(); } } void scheduleTraversals() { if (!mTraversalScheduled) { mTraversalScheduled = true; mTraversalBarrier = mHandler.getLooper().getQueue().postSyncBarrier(); // 会调用 mTraversalRunnable 中的 run 方法 mChoreographer.postCallback( Choreographer.CALLBACK_TRAVERSAL, mTraversalRunnable, null); if (!mUnbufferedInputDispatch) { scheduleConsumeBatchedInput(); } notifyRendererOfFramePending(); pokeDrawLockIfNeeded(); } } final class TraversalRunnable implements Runnable { @Override public void run() { doTraversal(); } } void doTraversal() { if (mTraversalScheduled) { mTraversalScheduled = false; mHandler.getLooper().getQueue().removeSyncBarrier(mTraversalBarrier); if (mProfile) { Debug.startMethodTracing("ViewAncestor"); } // 终于到了关键方法了: performTraversals(); if (mProfile) { Debug.stopMethodTracing(); mProfile = false; } } }ViewRootImpl 最终调用到了performTraversals 中,这个方法巨长,涉及到了 onMeasure/onLayout/onDraw 等重要方法的起源:
private void performTraversals() { ... // 这里最终会触发 view 的 onMeasure performMeasure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec); performLayout(lp, mWidth, mHeight); performDraw(); ... mIsInTraversal = false; }看到上面就是对应着 View 的绘制流程了,继续看 performDraw 的实现:
private void performDraw() { ... try { draw(fullRedrawNeeded); } finally { mIsDrawing = false; Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_VIEW); } ... } private void draw(boolean fullRedrawNeeded) { if (!drawSoftware(surface, mAttachInfo, xOffset, yOffset, scalingRequired, dirty)) { return; } } private boolean drawSoftware(Surface surface, AttachInfo attachInfo, int xoff, int yoff, boolean scalingRequired, Rect dirty) { ... try { canvas.translate(-xoff, -yoff); if (mTranslator != null) { mTranslator.translateCanvas(canvas); } canvas.setScreenDensity(scalingRequired ? mNoncompatDensity : 0); attachInfo.mSetIgnoreDirtyState = false; // 最终调用了 View 的 draw 方法了 mView.draw(canvas); } finally { ... } return true; }看到终于调用到 View 的 draw 方法来了,继续看下 ViewGroup 和 View 在这方法中的处理方式:
// View 中的 draw 方法: public void draw(Canvas canvas) { final int privateFlags = mPrivateFlags; final boolean dirtyOpaque = (privateFlags & PFLAG_DIRTY_MASK) == PFLAG_DIRTY_OPAQUE && (mAttachInfo == null || !mAttachInfo.mIgnoreDirtyState); mPrivateFlags = (privateFlags & ~PFLAG_DIRTY_MASK) | PFLAG_DRAWN; /* * Draw traversal performs several drawing steps which must be executed * in the appropriate order: * * 1. Draw the background * 2. If necessary, save the canvas' layers to prepare for fading * 3. Draw view's content * 4. Draw children * 5. If necessary, draw the fading edges and restore layers * 6. Draw decorations (scrollbars for instance) */ // Step 1, draw the background, if needed int saveCount; if (!dirtyOpaque) { drawBackground(canvas); } // skip step 2 & 5 if possible (common case) final int viewFlags = mViewFlags; boolean horizontalEdges = (viewFlags & FADING_EDGE_HORIZONTAL) != 0; boolean verticalEdges = (viewFlags & FADING_EDGE_VERTICAL) != 0; if (!verticalEdges && !horizontalEdges) { // Step 3, draw the content if (!dirtyOpaque) onDraw(canvas); // Step 4, draw the children dispatchDraw(canvas); drawAutofilledHighlight(canvas); // Overlay is part of the content and draws beneath Foreground if (mOverlay != null && !mOverlay.isEmpty()) { mOverlay.getOverlayView().dispatchDraw(canvas); } // Step 6, draw decorations (foreground, scrollbars) onDrawForeground(canvas); // Step 7, draw the default focus highlight drawDefaultFocusHighlight(canvas); if (debugDraw()) { debugDrawFocus(canvas); } // we're done... return; } /* * Here we do the full fledged routine... * (this is an uncommon case where speed matters less, * this is why we repeat some of the tests that have been * done above) */ boolean drawTop = false; boolean drawBottom = false; boolean drawLeft = false; boolean drawRight = false; float topFadeStrength = 0.0f; float bottomFadeStrength = 0.0f; float leftFadeStrength = 0.0f; float rightFadeStrength = 0.0f; // Step 2, save the canvas' layers int paddingLeft = mPaddingLeft; final boolean offsetRequired = isPaddingOffsetRequired(); if (offsetRequired) { paddingLeft += getLeftPaddingOffset(); } int left = mScrollX + paddingLeft; int right = left + mRight - mLeft - mPaddingRight - paddingLeft; int top = mScrollY + getFadeTop(offsetRequired); int bottom = top + getFadeHeight(offsetRequired); if (offsetRequired) { right += getRightPaddingOffset(); bottom += getBottomPaddingOffset(); } final ScrollabilityCache scrollabilityCache = mScrollCache; final float fadeHeight = scrollabilityCache.fadingEdgeLength; int length = (int) fadeHeight; // clip the fade length if top and bottom fades overlap // overlapping fades produce odd-looking artifacts if (verticalEdges && (top + length > bottom - length)) { length = (bottom - top) / 2; } // also clip horizontal fades if necessary if (horizontalEdges && (left + length > right - length)) { length = (right - left) / 2; } if (verticalEdges) { topFadeStrength = Math.max(0.0f, Math.min(1.0f, getTopFadingEdgeStrength())); drawTop = topFadeStrength * fadeHeight > 1.0f; bottomFadeStrength = Math.max(0.0f, Math.min(1.0f, getBottomFadingEdgeStrength())); drawBottom = bottomFadeStrength * fadeHeight > 1.0f; } if (horizontalEdges) { leftFadeStrength = Math.max(0.0f, Math.min(1.0f, getLeftFadingEdgeStrength())); drawLeft = leftFadeStrength * fadeHeight > 1.0f; rightFadeStrength = Math.max(0.0f, Math.min(1.0f, getRightFadingEdgeStrength())); drawRight = rightFadeStrength * fadeHeight > 1.0f; } saveCount = canvas.getSaveCount(); int solidColor = getSolidColor(); if (solidColor == 0) { final int flags = Canvas.HAS_ALPHA_LAYER_SAVE_FLAG; if (drawTop) { canvas.saveLayer(left, top, right, top + length, null, flags); } if (drawBottom) { canvas.saveLayer(left, bottom - length, right, bottom, null, flags); } if (drawLeft) { canvas.saveLayer(left, top, left + length, bottom, null, flags); } if (drawRight) { canvas.saveLayer(right - length, top, right, bottom, null, flags); } } else { scrollabilityCache.setFadeColor(solidColor); } // Step 3, draw the content if (!dirtyOpaque) onDraw(canvas); // Step 4, draw the children dispatchDraw(canvas); // Step 5, draw the fade effect and restore layers final Paint p = scrollabilityCache.paint; final Matrix matrix = scrollabilityCache.matrix; final Shader fade = scrollabilityCache.shader; if (drawTop) { matrix.setScale(1, fadeHeight * topFadeStrength); matrix.postTranslate(left, top); fade.setLocalMatrix(matrix); p.setShader(fade); canvas.drawRect(left, top, right, top + length, p); } if (drawBottom) { matrix.setScale(1, fadeHeight * bottomFadeStrength); matrix.postRotate(180); matrix.postTranslate(left, bottom); fade.setLocalMatrix(matrix); p.setShader(fade); canvas.drawRect(left, bottom - length, right, bottom, p); } if (drawLeft) { matrix.setScale(1, fadeHeight * leftFadeStrength); matrix.postRotate(-90); matrix.postTranslate(left, top); fade.setLocalMatrix(matrix); p.setShader(fade); canvas.drawRect(left, top, left + length, bottom, p); } if (drawRight) { matrix.setScale(1, fadeHeight * rightFadeStrength); matrix.postRotate(90); matrix.postTranslate(right, top); fade.setLocalMatrix(matrix); p.setShader(fade); canvas.drawRect(right - length, top, right, bottom, p); } canvas.restoreToCount(saveCount); drawAutofilledHighlight(canvas); // Overlay is part of the content and draws beneath Foreground if (mOverlay != null && !mOverlay.isEmpty()) { mOverlay.getOverlayView().dispatchDraw(canvas); } // Step 6, draw decorations (foreground, scrollbars) onDrawForeground(canvas); }这个方法的大体意思是这样的:
@Override public void draw(Canvas canvas) { ... drawBackground(canvas); // 绘制背景 onDraw(canvas); // 调用自己的 onDraw 方法来绘制内容 dispatchDraw(canvas); // 分发绘制 onDrawForeground(canvas); // 绘制前景 ... }上面几个方法中,只有 dispatchDraw 涉及到分发绘制,其他的都是对自身的绘制,所以继续看 dispatchDraw
// View 中的实现,是个空方法,也就是 View 没有孩子,不需要什么分发 protected void dispatchDraw(Canvas canvas) { }View 中的实现,是个空方法,也就是 View 没有孩子,不需要什么分发。那么看下 ViewGroup 中是怎么分发的:
@Override protected void dispatchDraw(Canvas canvas) { ... while (transientIndex >= 0) { // there may be additional transient views after the normal views final View transientChild = mTransientViews.get(transientIndex); if ((transientChild.mViewFlags & VISIBILITY_MASK) == VISIBLE || transientChild.getAnimation() != null) { // 看到这里,会去绘制 子View more |= drawChild(canvas, transientChild, drawingTime); } transientIndex++; if (transientIndex >= transientCount) { break; } } ... } protected boolean drawChild(Canvas canvas, View child, long drawingTime) { // 又调回了 View 的 draw 来了 return child.draw(canvas, this, drawingTime); }上面又调会了 View 的 draw 来了,如此递归调用下去,直到遍历完所有的 VIew 。
4. 总结
1 invalidate 和 postInvalidate 的关系:
postInvalidate 最终通过 Handler 切换到主线程,调用 invalidate
2 能否在子线程中更新 UI ?
只要在校验 UI 线程前,子线程是可以更新 UI 的,也就是 Activity 的 onResume 方法前。因为在 onResume 中创建了 ViewRootImpl。
3 invalidate 源码
invalidate 会先找到父类去走绘制流程,最终遍历所有相关联的 View ,触发它们的 onDraw 方法进行绘制
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持VEVB武林网。
新闻热点
疑难解答