有时我们需要较为实时的查看服务器上的网卡流量,这里我写了两个小脚本,一个用shell(先写的,一次只能查看一个网卡),另一个用Python(后写的,一次可查看多个网卡)。
脚本中都用了while true“死循环”,每隔10s从“/proc/net/dev”中取一次值并根据10s内的差值计算10s内的平均带宽;按ctrl+c停止执行。脚本兼容centos6和7
两个脚本都不太复杂,而且脚本中注释也比较细致,所以我就不过多解释脚本内容了。
直接上图上脚本:
shell版–使用截图:
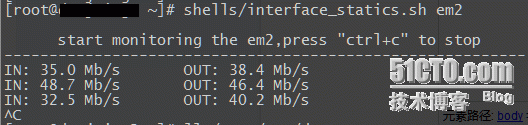
shell版代码:
#!/bin/sh#by ljk 20160526if [ "$1" = "" ];then #判断后面是否有跟参数 echo -e "/n use interface_name after the script,like /"script eth0/".../n" exit -1fiecho -e "/n start monitoring the $1,press /"ctrl+c/" to stop"echo ----------------------------------------------------------file=/proc/net/dev #内核网卡信息文件while true do RX_bytes=`cat $file|grep $1|sed 's/^ *//g'|awk -F'[ :]+' '{print $2}'` #这里sed这一步为了同时兼容centos6和7 TX_bytes=`cat $file|grep $1|sed 's/^ *//g'|awk -F'[ :]+' '{print $10}'` sleep 10 RX_bytes_later=`cat $file|grep $1|sed 's/^ *//g'|awk -F'[ :]+' '{print $2}'` TX_bytes_later=`cat $file|grep $1|sed 's/^ *//g'|awk -F'[ :]+' '{print $10}'` #B*8/1024/1024=Mb speed_RX=`echo "scale=2;($RX_bytes_later - $RX_bytes)*8/1024/1024/10"|bc` speed_TX=`echo "scale=2;($TX_bytes_later - $TX_bytes)*8/1024/1024/10"|bc` printf "%-3s %-3.1f %-10s %-4s %-3.1f %-4s/n" IN: $speed_RX Mb/s OUT: $speed_TX Mb/sdonePython版–使用截图:
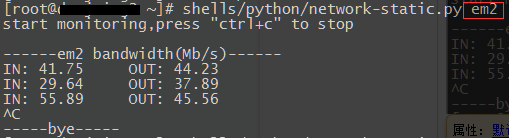
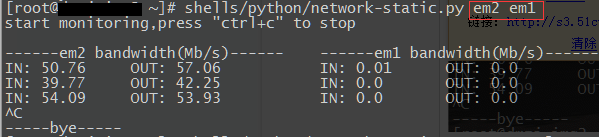
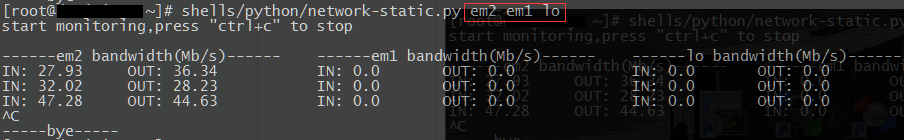
Python版代码:
#!/bin/env python3 #by ljk 20160526 import os,re,sys,time if len(sys.argv) == 1: print('/n使用方法:请跟上网卡名称,可接"单个网卡"/"多个网卡,以空格分开"./n') sys.exit(100) else: print('start monitoring,press "ctrl+c" to stop/n') for arg in sys.argv[1:]: #输出标头 header = '------{} bandwidth(Mb/s)------'.format(arg) print(header.ljust(35),end='') print() #global values_dic values_dic = {} #定义空字典,用来在下面函数中存放各网卡的各项需要用到的值 def get_values(orders): try: with open('/proc/net/dev') as f: lines=f.readlines() #内容不多,一次性读取较方便 for arg in sys.argv[1:]: for line in lines: line=line.lstrip() #去掉行首的空格,以便下面split if re.match(arg,line): values = re.split("[ :]+",line) #以空格和:作为分隔符 values_dic[arg+'r'+orders]=values[1] #1为接收值 values_dic[arg+'t'+orders]=values[9] #9为发送值 #return [values[1],values[9]] #可返回列表 except (FileExistsError,FileNotFoundError,PermissionError): print('open file error') sys.exit(-1) try: while True: get_values('first') #第一次取值 time.sleep(10) get_values('second') #10s后第二次取值 for arg in sys.argv[1:]: r_bandwidth = (int(values_dic[arg+'r'+'second']) - int(values_dic[arg+'r'+'first']))/1024/1024/10*8 t_bandwidth = (int(values_dic[arg+'t'+'second']) - int(values_dic[arg+'t'+'first']))/1024/1024/10*8 print('IN: '+str(round(r_bandwidth,2)).ljust(8)+' OUT: '+str(round(t_bandwidth,2)).ljust(16),end='') print() values_dic = {} #清空本次循环后字典的内容 except KeyboardInterrupt: print("/n-----bye-----") 这俩脚本使用起来都还是很方便实用的,共享出来希望能给朋友们工作中带来一点方便。
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持VEVB武林网。
新闻热点
疑难解答