那么,servlet有什么问题?
既然jsp用来提供动态web内容并且对于从表现层中分离内容很不错,一些人也许想知道为什么servlet要从jsp中脱离出来与它并列。servlet的功用没有问题。它对于服务端处理干得很好,而且,由于它重要的已安装基础,就适合这个。实际上,从结构上说,你可以把jsp看作实现为servlet 2.1 api的扩展的servlet高级抽象。仍然不应该不加区别地使用servlet;它可能不会适用于每一个人。举个例子来说,尽管页面设计者能够很容易地使用常规html或者xml工具编写jsp页面,而servlet通常更适合后台开发者,他们通常使用某种ide——一个通常需要高层次的编程专门知识的过程。当发布servlet时,即使开发者也必须留意和确认在内容和表现之间没有紧耦合。通常,你可以通过加入第三方的html封装包比如htmlkona来做这个。即使这样做了,尽管带来了一些简单的对于屏幕变化的伸缩性,仍然不能为你防止免受表现格式自身的变化的影响。例如,如果你的表现形式从html转变到dhtml,你将仍然需要确认你的封装包是否兼容这种新格式。在最坏的情况下,如果封装包不能用了,你可能最终会在动态内容内部硬编码表现形式。那么,解决办法是什么?就像你你将要看到的,一个办法将会同时使用jsp和servlet来创建应用系统。
差异哲学
早期的jsp规范主张两种使用jsp技术创建应用的哲学思路。这两种思路,用术语来说就是jsp模式1和模式2,本质上的区别在于大部分请求的处理发生的位置。在模式1架构中,如图1所示,jsp页面独立地负责处理请求和发送反馈给客户端。这里仍然有内容和表现的分离,因为所有的数据访问是使用bean完成的。尽管模式1架构应该很适合简单应用,但是对于复杂的实现是不可取的。这种结构的任意使用通常会导致大量的脚本和java代码嵌入到jsp页面中,特别是在有大量的请求需要处理的情况下。尽管这可能对java开发者来说不是一个大问题,但是却无疑是一个问题,如果你的jsp页面是由设计师创建和维护的话——在大项目中通常如此。最终,这个问题甚至会导致角色定义和责任分配的混乱,引起本可以轻松避免的项目管理的麻烦。
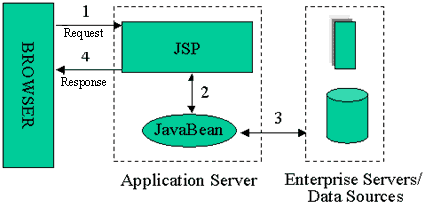
图1:jsp模式1结构
模式2架构如图2所示,是一个为动态内容服务的混合方案,因为它同时使用了servlet和jsp。它利用了两种技术的优势,使用jsp产生表现层而servlet负责执行敏感任务。在这里,servlet扮演控制器的角色,负责请求处理和产生jsp要使用的bean和对象,以及根据客户的动作决定下一步转发到哪一个jsp页面。特别要注意的是jsp页面内部并没有处理逻辑;它只是简单地负责取得可能是servelet事先创建的对象和bean,并为在了静态模版中插入从servlet释放出动态内容。我的观点是,这个办法一般会形成最干净彻底的表现与内容的分离,使得你的开发团队里的开发者和页面设计师的角色与责任能够清晰。实际上,你的应用越复杂,使用模式2带来的好处就越多。
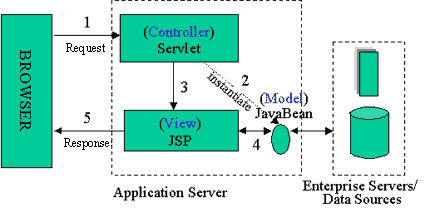
图2:jsp模式2结构
为了弄清模式2背后的概念,我们来参观一个细化的具体实现:一个叫做音乐无界的在线音乐商店样品。
了解音乐无界
主视图,或者说表现层,对于我们的音乐无界由jsp页面eshop.jsp产生(见清单1)。你会注意到这个页面几乎仅仅处理这个应用的主要用户界面,而且没有做任何处理工作——一个最佳的jsp脚本。也注意一下另一个jsp页面,cart.jsp(见清单2),通过指令<jsp:include page="cart.jsp" flush="true" />包含在eshop.jsp之内。
清单1 eshop.jsp |
| <%@ page session="true" %> <html> <head> <title>music without borders</title> </head> <body bgcolor="#33ccff"> <font face="times new roman,times" size="+3"> music without borders </font> <hr><p> <center> <form name="shoppingform" action="/examples/servlet/shoppingservlet" method="post"> <b>cd:</b> <select name=cd> <option>yuan | the guo brothers | china | $14.95</option> <option>drums of passion | babatunde olatunji | nigeria | $16.95</option> <option>kaira | tounami diabate| mali | $16.95</option> <option>the lion is loose | eliades ochoa | cuba | $13.95</option> <option>dance the devil away | outback | australia | $14.95</option> <option>record of changes | samulnori | korea | $12.95</option> <option>djelika | tounami diabate | mali | $14.95</option> <option>rapture | nusrat fateh ali khan | pakistan | $12.95</option> <option>cesaria evora | cesaria evora | cape verde | $16.95</option> <option>ibuki | kodo | japan | $13.95</option> </select> <b>quantity: </b><input type="text" name="qty" size="3" value=1> <input type="hidden" name="action" value="add"> <input type="submit" name="submit" value="add to cart"> </form> </center> <p> <jsp:include page="cart.jsp" flush="true" /> </body> </html> |
清单2 cart.jsp |
| <%@ page session="true" import="java.util.*, shopping.cd" %> <% vector buylist = (vector) session.getvalue("shopping.shoppingcart"); if (buylist != null && (buylist.size() > 0)) { %> <center> <table border="0" cellpadding="0" width="100%" bgcolor="#ffffff"> <tr> <td><b>album</b></td> <td><b>artist</b></td> <td><b>country</b></td> <td><b>price</b></td> <td><b>quantity</b></td> <td></td> </tr> <% for (int index=0; index < buylist.size();index++) { cd anorder = (cd) buylist.elementat(index); %> <tr> <td><b><%= anorder.getalbum() %></b></td> <td><b><%= anorder.getartist() %></b></td> <td><b><%= anorder.getcountry() %></b></td> <td><b><%= anorder.getprice() %></b></td> <td><b><%= anorder.getquantity() %></b></td> <td> <form name="deleteform" action="/examples/servlet/shoppingservlet" method="post"> <input type="submit" value="delete"> <input type="hidden" name= "delindex" value='<%= index %>'> <input type="hidden" name="action" value="delete"> </form> </td> </tr> <% } %> </table> <p> <form name="checkoutform" action="/examples/servlet/shoppingservlet" method="post"> <input type="hidden" name="action" value="checkout"> <input type="submit" name="checkout" value="checkout"> </form> </center> <% } %> |
这里,cart.jsp处理基于session的购物车的表现形式,它指定了我们的mvc结构中的模型。观察cart.jsp开头这一段脚本:
<%
vector buylist = (vector) session.getvalue("shopping.shoppingcart");
if (buylist != null && (buylist.size() > 0)) {
%>
基本上,这段脚本从session中提出了购物车。如果购物车为空或者还未创建,它不会显示任何东西;因此,当用户第一次访问的时候,他见到的页面如图3。
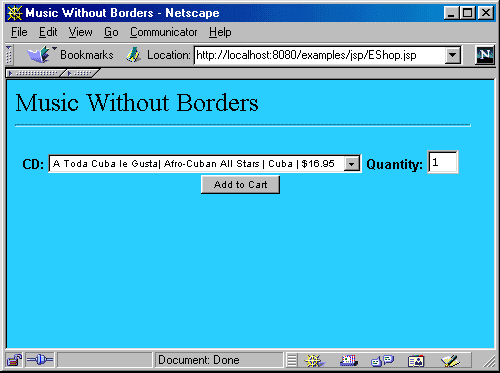
图3:音乐无界,主视图
如果购物车不是空的,那么已选中的物品会一次一个地从购物车中被提出,像下面的脚本示范的那样:
<%
for (int index=0; index < buylist.size(); index++) {
cd anorder = (cd) buylist.elementat(index);
%>
一旦描述物品的变量已创建,它们就简单地被jsp表达式插入到静态html模版中去。图4显示了用户已经放了一些东西到购物车里去是的情况。
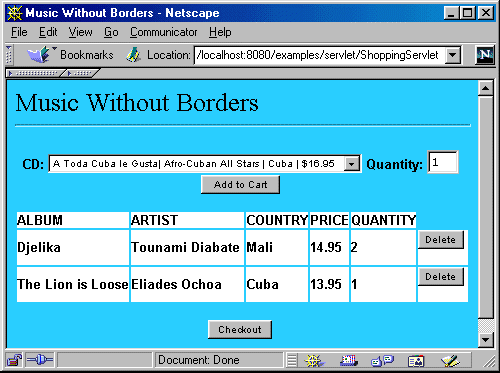
图4:音乐无界,购物车视图
这里要注意的重要的一件事是对所有动作的处理既不发生在eshop.jsp也不在cart.jsp里,而是由控制器servlet,shoppingservlet.java处理,见清单3:
清单3 shoppingservlet.java |
| import java.util.*; import java.io.*; import javax.servlet.*; import javax.servlet.http.*; import shopping.cd; public class shoppingservlet extends httpservlet { public void init(servletconfig conf) throws servletexception { super.init(conf); } public void dopost (httpservletrequest req, httpservletresponse res) throws servletexception, ioexception { httpsession session = req.getsession(false); if (session == null) { res.sendredirect("http://localhost:8080/error.html"); } vector buylist= (vector)session.getvalue("shopping.shoppingcart"); string action = req.getparameter("action"); if (!action.equals("checkout")) { if (action.equals("delete")) { string del = req.getparameter("delindex"); int d = (new integer(del)).intvalue(); buylist.removeelementat(d); } else if (action.equals("add")) { //any previous buys of same cd? boolean match=false; cd acd = getcd(req); if (buylist==null) { //add first cd to the cart buylist = new vector(); //first order buylist.addelement(acd); } else { // not first buy for (int i=0; i< buylist.size(); i++) { cd cd = (cd) buylist.elementat(i); if (cd.getalbum().equals(acd.getalbum())) { cd.setquantity(cd.getquantity()+acd.getquantity()); buylist.setelementat(cd,i); match = true; } //end of if name matches } // end of for if (!match) buylist.addelement(acd); } } session.putvalue("shopping.shoppingcart", buylist); string url="/jsp/shopping/eshop.jsp"; servletcontext sc = getservletcontext(); requestdispatcher rd = sc.getrequestdispatcher(url); rd.forward(req, res); } else if (action.equals("checkout")) { float total =0; for (int i=0; i< buylist.size();i++) { cd anorder = (cd) buylist.elementat(i); float price= anorder.getprice(); int qty = anorder.getquantity(); total += (price * qty); } total += 0.005; string amount = new float(total).tostring(); int n = amount.indexof('.'); amount = amount.substring(0,n+3); req.setattribute("amount",amount); string url="/jsp/shopping/checkout.jsp"; servletcontext sc = getservletcontext(); requestdispatcher rd = sc.getrequestdispatcher(url); rd.forward(req,res); } } private cd getcd(httpservletrequest req) { //imagine if all this was in a scriptlet...ugly, eh? string mycd = req.getparameter("cd"); string qty = req.getparameter("qty"); stringtokenizer t = new stringtokenizer(mycd,"|"); string album= t.nexttoken(); string artist = t.nexttoken(); string country = t.nexttoken(); string price = t.nexttoken(); price = price.replace('$',' ').trim(); cd cd = new cd(); cd.setalbum(album); cd.setartist(artist); cd.setcountry(country); cd.setprice((new float(price)).floatvalue()); cd.setquantity((new integer(qty)).intvalue()); return cd; } } |
清单4 cd.java |
| package shopping; public class cd { string album; string artist; string country; float price; int quantity; public cd() { album=""; artist=""; country=""; price=0; quantity=0; } public void setalbum(string title) { album=title; } public string getalbum() { return album; } public void setartist(string group) { artist=group; } public string getartist() { return artist; } public void setcountry(string cty) { country=cty; } public string getcountry() { return country; } public void setprice(float p) { price=p; } public float getprice() { return price; } public void setquantity(int q) { quantity=q; } public int getquantity() { return quantity; } } |
注意我们在这个servlet中还包括了额外的智能,因此它能够知道如果选择了一张已在购物车中的cd,那么应该简单地增加session中cd bean的计数。它也处理从cart.jsp中触发的动作,比如用户从购物车中删除物品,或是继续去收银台结帐。注意控制器总是对哪个资源应该被调用来对特定的动作产生回馈有完全的控制权。例如,对购物车状态的改变,像增加和删除,会引起控制器将请求处理后转发给eshop.jsp页面。这样引起该页面依照已更新的购物车依次重新显示主视图。如果用户决定结帐,则请求被处理后转发给checkout.jsp(见清单5),通过后面的请求分配器,象下面显示的这样:
string url="/jsp/shopping/checkout.jsp";
servletcontext sc = getservletcontext();
requestdispatcher rd = sc.getrequestdispatcher(url);
rd.forward(req,res);
清单5 checkout.jsp |
| <%@ page session="true" import="java.util.*, shopping.cd" %> <html> <head> <title>music without borders checkout</title> </head> <body bgcolor="#33ccff"> <font face="times new roman,times" size=+3> music without borders checkout </font> <hr><p> <center> <table border="0" cellpadding="0" width="100%" bgcolor="#ffffff"> <tr> <td><b>album</b></td> <td><b>artist</b></td> <td><b>country</b></td> <td><b>price</b></td> <td><b>quantity</b></td> <td></td> </tr> <% vector buylist = (vector) session.getvalue("shopping.shoppingcart"); string amount = (string) request.getattribute("amount"); for (int i=0; i < buylist.size();i++) { cd anorder = (cd) buylist.elementat(i); %> <tr> <td><b><%= anorder.getalbum() %></b></td> <td><b><%= anorder.getartist() %></b></td> <td><b><%= anorder.getcountry() %></b></td> <td><b><%= anorder.getprice() %></b></td> <td><b><%= anorder.getquantity() %></b></td> </tr> <% } session.invalidate(); %> <tr> <td> </td> <td> </td> <td><b>total</b></td> <td><b>$<%= amount %></b></td> <td> </td> </tr> </table> <p> <a href="/examples/jsp/shopping/eshop.jsp">shop some more!</a> </center> </body> </html> |
checkout.jsp仅仅从session中提出购物车并为此请求提取出总金额,然后显示选中的物品和他们的总价格。图5显示了结算时的用户视图。一旦用户去结帐,删除session对象是同样重要的。这个由页面末端的session.invalidate()调用来完成。有两个理由必须这样做。第一,如果没有使session无效,用户的购物车不会重新初始化;如果用户结帐后试图开始新一轮的采购,她的购物车会继续保存着已经付过钱的物品。第二,如果用户结帐后仅仅是离开了网站,这个session对象不会被垃圾收集机制回收而是继续占用宝贵的系统资源直到租约到期。因为缺省的session租约时间是大约三十分钟,在一个大容量系统上这将会很快导致系统内存耗尽。当然,我们都知道对一个耗尽了系统内存的应用程序会发生什么。
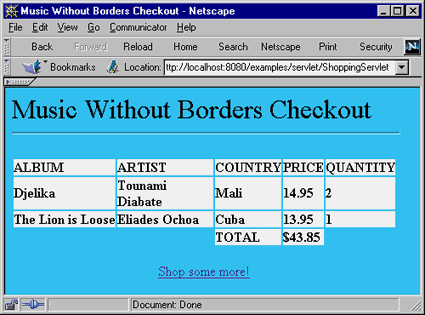
图5:结账视图
注意这个应用所有的资源都是session相关的,因为这里的模式存储在session里。因此,你必须确保用户不会因为某些原因甚至由于错误直接访问控制器。你可以在控制器检测到缺少有效session的时候让客户端自动转向到一个错误页面(见列表6),来避免这种情况的发生。
列表6 error.html |
| <html> <body> <h1> sorry, there was an unrecoverable error! <br> please try <a href="/examples/jsp/shopping/eshop.jsp">again</a>. </h1> </body> </html> |
部署音乐无界
我假定你正在使用来自sun的最新版本的javaserver web development kit (jswdk)来运行这个例子。如果不是,参看资源小节去看看到哪里取得它。假设服务器安装在/jswdk-1.0.1,这是microsoft windows系统下的缺省路径,可以象下面这样部署音乐无界应用:
create shopping directory under /jswdk-1.0.1/examples/jsp
copy eshop.jsp to /jswdk-1.0.1/examples/jsp/shopping
copy cart.jsp to /jswdk-1.0.1/examples/jsp/shopping
copy checkout.jsp to /jswdk-1.0.1/examples/jsp/shopping
compile the .java files by typing javac *.java
copy shoppingservlet.class to /jswdk-1.0.1/webpages/web-inf/servlets
create shopping directory under /jswdk-1.0.1/examples/web-inf/jsp/beans
copy cd.class to /jswdk-1.0.1/examples/web-inf/jsp/beans/shopping
copy error.html to /jswdk-1.0.1/webpages
once your server has been started, you should be able to access the application using http://localhost:8080/examples/jsp/shopping/eshop.jsp as the url
只要你的服务器启动,你应该可以使用url http://localhost:8080/examples/jsp/shopping/eshop.jsp来访问这个应用程序。
利用jsp和servlet
着这个例子里,我们从细节上检查了控制的层次和模式2架构提供的灵活性。实际上,我们已经看到了servlet和jsp页面最好的特性是如何开发出最大化的内容与表现的剥离。只要正确地应用,模式2架构会将所有的处理逻辑集中到控制器servlet手里,而jsp页面只负责视图或者说表现层的工作。然而,使用模式2结构的阻力在于它的复杂性。因此,对于简单应用使用模式1也是可以接受的。
新闻热点
疑难解答