jsp提供了很多简单实用的工具,其中包括从数据库中读出数据,发送数据,并能够把结果显示在一个饼状图形。现在让我们看看这一简单而实用的方法。
你所需要的东西
为了能正确运行这一文章相关的范例,你必须需要jdk 1.2或更高的版本、一个关系数据库管理系统、一个jsp网络服务器。我都是在tomcat调试这些例子,同时我也使用了sun java 2 sdk发布的com.sun.image.codec.jpegclasses。
数据库设计
假设你在一家从事销售新鲜水果的公司上班,公司出售的水果包括:苹果、桔子、葡萄。现在你的老板想用一个饼状图形显示每一种水果的总出售量,饼状图形能使每一种产品的销售情况一目了然,老板可以迅速掌握公司的产品成交情况。
表a使用了本文中的两种数据库列表。第一种列表(products)包含所有销售产品的名称;第二种列表(sales)包含每一种产品对应的销售量。
listing a
database design
---------------
p_products table
----------------
productid int (number) not null
productname string (varchar) not null
p_sales table
-------------
saleid int (number) not null
productid int (number) not null
amount float not null
产品(products)列表包含productid和productname两个域。销售(sales)列表包含saleid, productid,以及总额。销售列表中的productid提供了这两个列表之间的关联。销售列表中的总额包含了每一次出售的现金数额,这些数额以浮点型数据出现。
表b中的getproducts()方法连接了两个数据库,并把所有的产品名称保存在数组中:
listing b
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//get products from the database as a string array
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
public string[] getproducts()
{
string[] arr = new string[0];
connection con;
statement stmt;
resultset rs;
int count = 0;
string sql = "select * from p_products order by productid";
try
{
//load driver: class.forname(driver);
//connect to the database with the url
con = drivermanager.getconnection(dburl , dbuid , dbpwd);
stmt = con.createstatement();
//get resultset
rs = stmt.executequery(sql);
//count the records
while(rs.next())
{count++;}
//create an array of the correct size
arr = new string[count];
//get resultset (the portable way of using rs a second time)
rs = stmt.executequery(sql);
while(rs.next())
{
arr[rs.getint("productid")] = rs.getstring("productname");
}
stmt.close();
con.close();
}
catch (java.lang.exception ex)
{
arr[0] = ex.tostring();
}
return arr;
}
我设置以下的数据库规则:
1、productid在产品列表中最独特,也是最关键;
2、productid对于第一个记录的值为0;
3、所有之后的连续的记录都是累加的,所以第二个记录的productid为1,第三个记录的productid为2,以此类推。
这些数据库规则允许在product数组中存储数据,如下所示:
arr[rs.getint("productid")] = rs.getstring("productname");
一些数据库管理系统在缺省情况下就允许数据的自动累加或者自动排序。当你在设计数据库时,一定先查明你的数据库管理系统遵循哪些规则,比如自动累加,自动排序等。
获取总销售量
在多数情况下,销售列表中会有很多个记录,所以访问数据库的快捷性和高效性显得非常重要。现在我们只需要访问数据库中每一种产品的总额销售量。
表c中的getsales()方法与数据库连接并返回一个数组,这个数组包含每一种产品的总额出售量。
listing c
| //////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// //get the sales totals from the database //////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// public float[] getsales(int products) { float[] arr = new float[products]; connection con; statement stmt; resultset rs; int count = 0; string sql = "select productid, amount from p_sales"; try { //load driver: class.forname(driver); //connect to the database with the url con = drivermanager.getconnection(dburl , dbuid , dbpwd); stmt = con.createstatement(); //get resultset rs = stmt.executequery(sql); while(rs.next()) { int product = rs.getint("productid"); //check that the productid is valid if (product >= 0 && product < products) { //add to product total arr[product] += rs.getfloat("amount"); count++; } } stmt.close(); con.close(); } catch (java.lang.exception ex) { arr[0] = -1.0f; } return arr; } |
| int product = rs.getint("productid"); arr[product] += rs.getfloat("amount"); |
| color piecolorarray[] = {new color(210,60,60), new color(60,210,60)…} |
| curpiecolor++; if(curpiecolor >= piecolorarray.length) {curpiecolor = 0;} |
| renderinghints renderhints = new renderinghints(renderinghints.key_antialiasing, renderinghints.value_antialias_on); g2d.setrenderinghints(renderhints); |
制做可调整的边界
图a中的饼状图形有一边界,如何能改变边界的大小呢?可以先定义int border = 10,然后计算边界内面积的大小而实现:
ellipse2d.double elb = new ellipse2d.double(x_pie - border/2, y_pie - border/2, piewidth + border, pieheight + border);
x_pie和y_pie的值代表着包围在饼状图形的正方形的左上角。我们通过边界面积取一半(border/2)而得到饼状图形的中心。
圆弧(arc)理论
从java.awt.graphics 类继承而来的fillarc()方法提供了绘制饼状图形各个部分(或圆弧)的简单方法:
| g2d.fillarc(x_position, y_position, width, height, startangle, sweepangle); |
x_position,和y_position整数代表着要填充的圆弧的左上角的x,y的坐标,width和heigh整数代表其具体的尺寸。如果width和height的值相等,饼状图形将是一个圆。如果width和height不相等,那么饼状图形将是一个椭圆。
fillarc()方法决定基于sweepangle整数值的圆弧的大小。如果sweepangle值是正的,则圆弧是以反时针方向绘制,反之以顺时针绘制。
绘制圆弧
第一步,使用piecolor对象的getpiecolor()方法获取最近饼状圆弧的颜色,并把它赋予当前的圆弧::
| g2d.setcolor(pc.getpiecolor()); |
接着,通过不断循环sales[]数组并使其累加而获得总共的销售量:
| salestotal += sales[i]; |
使用总共销售量,可以计算出每一种产品销售情况占总共销售量的百分量:
| float perc = (sales[i]/salestotal); |
我们计算sweepangle即可给圆弧的每一部分分配度数:
| int sweepangle = (int)(perc * 360); |
每一部分圆弧画完之后,startangle即可根据当前的sweepangle递增。这就确保当前的圆弧部分都是以上一圆弧为开始,从而建立一个完整的饼状图形。
显示图标
图标提供了显示饼状图形中各个部分最简洁的方式。一个图标的大小应该与饼状图形中的占有量相对应。
图b显示了一个完整饼状图形及其对应各个部分的图标,包括产品名称、销售总量、以及各个部分的占有量。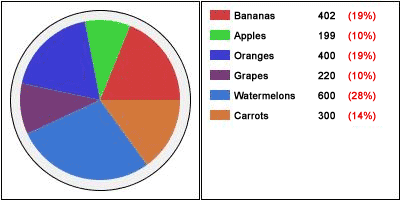
图b
总结
本文讲述了如何利用jsp绘制饼状图形的方法及算法,这些方法及算法简单而实用,开发人员可以充分地利用这些方法。
附:本文全部源代码
listing e
| <%@ page language="java" %> <%@ page import="java.io.outputstream" %> <%@ page import="java.sql.*" %> <%@ page import="java.awt.*" %> <%@ page import="java.awt.geom.*" %> <%@ page import="java.awt.image.bufferedimage" %> <%@ page import="com.sun.image.codec.jpeg.*" %> <%! //////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// // piecolors class manages the colors used in the pie chart //////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// class piecolors { color piecolorarray[] = { new color(210,60,60), new color(60,210,60), new color(60,60,210), new color(120,60,120), new color(60,120,210), new color(210,120,60) }; int curpiecolor = 0; public color getpiecolor() { return piecolorarray[curpiecolor]; } public void setnewcolor() { curpiecolor++; if(curpiecolor >= piecolorarray.length) {curpiecolor = 0;} } } %> <%! string driver = "com.mysql.jdbc.driver"; string dburl = "jdbc:mysql://localhost/articles"; string dbuid = "myuid"; string dbpwd = "mypwd"; //////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// // get the products from the database as a string array //////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// public string[] getproducts() { string[] arr = new string[0]; connection con; statement stmt; resultset rs; int count = 0; string sql = "select * from p_products order by productid"; try { //load driver: class.forname(driver); //connect to the database with the url con = drivermanager.getconnection(dburl , dbuid , dbpwd); stmt = con.createstatement(); //get resultset rs = stmt.executequery(sql); //count the records while(rs.next()){count++; } //create an array of the correct size arr = new string[count]; //get resultset (the most portable way of using rs a second time) rs = stmt.executequery(sql); while(rs.next()) { arr[rs.getint("productid")] = rs.getstring("productname"); } stmt.close(); con.close(); } catch (java.lang.exception ex) {arr[0] = ex.tostring();} return arr; } //////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// //get the sales totals from the database //////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// public float[] getsales(int products) { float[] arr = new float[products]; connection con; statement stmt; resultset rs; string sql = "select productid, amount from p_sales"; try { //load driver: class.forname(driver); //connect to the database with the url con = drivermanager.getconnection(dburl , dbuid , dbpwd); stmt = con.createstatement(); //get resultset rs = stmt.executequery(sql); while (rs.next()) { int product = rs.getint("productid"); //check that the productid is valid if (product >= 0 && product < products) { //add to product total arr[product] += rs.getfloat("amount"); } } stmt.close(); con.close(); } catch (java.lang.exception ex) {arr[0] = -1.0f; } return arr; } %> <% //get an array that contains the product names string products[] = getproducts(); //read the data and store the totals in an array float sales[] = getsales(products.length); //declare piecolors piecolors pc = new piecolors(); //colors color dropshadow = new color(240,240,240); //inner padding to make sure bars never touch the outer border int inneroffset = 20; //set the graph's outer width & height int width = 400; int height = 200; int pieheight = height - (inneroffset * 2); int piewidth = pieheight; //to make a square (circular) pie int halfwidth = width/2; //width of the inner graphable area int innerwidth = width - (inneroffset * 2); //graph dimensions dimension graphdim = new dimension(width,height); rectangle graphrect = new rectangle(graphdim); //border dimensions dimension borderdim = new dimension(halfwidth-2,height-2); rectangle borderrect = new rectangle(borderdim); ///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// //set up the graph //////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// //set content type response.setcontenttype("image/jpeg"); //create bufferedimage & graphics2d bufferedimage bi = new bufferedimage(width, height, bufferedimage.type_int_rgb); graphics2d g2d = bi.creategraphics(); // set antialiasing renderinghints renderhints = new renderinghints( renderinghints.key_antialiasing,renderinghints.value_antialias_on); g2d.setrenderinghints(renderhints); //set graph background color to white: g2d.setcolor(color.white); g2d.fill(graphrect); //draw black border g2d.setcolor(color.black); borderrect.setlocation(1,1); g2d.draw(borderrect); //now draw border for legend borderrect.setlocation((width/2) + 1,1); g2d.draw(borderrect); //////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// //draw data onto the graph: //////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// int x_pie = inneroffset; int y_pie = inneroffset; int border = 20; //main chart ellipse //ellipse2d.double el = new ellipse2d.double(x_pie, y_pie, piewidth, pieheight); ellipse2d.double elb = new ellipse2d.double(x_pie - border/2, y_pie - border/2, piewidth + border, pieheight + border); //shadow g2d.setcolor(dropshadow); g2d.fill(elb); //border g2d.setcolor(color.black); g2d.draw(elb); ///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// //calculate the total sales ///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// float salestotal = 0.0f; int lastelement = 0; for(int i=0; i<products.length; i++) { if(sales[i] > 0.0f) { salestotal += sales[i]; lastelement = i; } } ////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// //draw the pie chart ///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// //chart variables int startangle = 0; //legend variables int legendwidth = 20; int x_legendtext = halfwidth + inneroffset/2 + legendwidth + 5; int x_legendbar = halfwidth + inneroffset/2; int textheight = 20; int curelement = 0; int y_legend = 0; //dimensions of the legend bar dimension legenddim = new dimension(legendwidth , textheight/2); rectangle legendrect = new rectangle(legenddim); for(int i=0; i<products.length; i++) { if(sales[i] > 0.0f) { //calculate percentage sales float perc = (sales[i]/salestotal); //calculate new angle int sweepangle = (int)(perc * 360); //check that the last element goes back to 0 position if (i == lastelement) { sweepangle = 360-startangle; } // draw arc g2d.setcolor(pc.getpiecolor()); g2d.fillarc(x_pie, y_pie, piewidth, pieheight, startangle, sweepangle); //increment startangle with the sweepangle startangle += sweepangle; ///////////// //draw legend ///////////// //set y position for bar y_legend = curelement * textheight + inneroffset; //display the current product string display = products[i]; g2d.setcolor(color.black); g2d.drawstring(display, x_legendtext, y_legend); //display the total sales display = "" + (int)sales[i]; g2d.setcolor(color.black); g2d.drawstring(display, x_legendtext + 80, y_legend); //display the sales percentage display = " (" + (int)(perc*100) + "%)"; g2d.setcolor(color.red); g2d.drawstring(display, x_legendtext + 110, y_legend); //draw the bar g2d.setcolor(pc.getpiecolor()); legendrect.setlocation(x_legendbar,y_legend - textheight/2); g2d.fill(legendrect); //set new pie color pc.setnewcolor(); //increment curelement++; } } //////////////////////////////////////////////// // encode the graph ///////////////////////////////////////// outputstream output = response.getoutputstream(); jpegimageencoder encoder = jpegcodec.createjpegencoder(output); encoder.encode(bi); output.close(); %> |
新闻热点
疑难解答