arcengine geometry库定义了基本几何图形的矢量表达形式,顶级的几何图形有points、multipoints、polylines、polygons、 multipatches,geodatabase和绘图系统使用这些几何图形来定义其他各种形状的特征和图形,提供了编辑图形的操作方法和地图符号系统符号化特征数据的途径。
geometry库中几个核心类和接口构成了geometry对象的基本框架。
geometryenvironment
geometryenvironment提供了从不同的输入、设置或获取全局变量来创建几何图形的方法,以便控制geometry方法的行为。geometryenvironment对象是一个单例对象。
以下为引用的内容: public ipolyline testgeometryenvironment() public ipolyline testgeometryenvironment()   { {  ispatialreferencefactory spatialreferencefactory = new spatialreferenceenvironmentclass(); ispatialreferencefactory spatialreferencefactory = new spatialreferenceenvironmentclass();  //create a projected coordinate system and define its domain, resolution, and x,y tolerance. //create a projected coordinate system and define its domain, resolution, and x,y tolerance. ispatialreferenceresolution spatialreferenceresolution = spatialreferencefactory.createprojectedcoordinatesystem((int)esrisrprojcstype.esrisrprojcs_nad1983utm_11n) as ispatialreferenceresolution; ispatialreferenceresolution spatialreferenceresolution = spatialreferencefactory.createprojectedcoordinatesystem((int)esrisrprojcstype.esrisrprojcs_nad1983utm_11n) as ispatialreferenceresolution;  spatialreferenceresolution.constructfromhorizon(); spatialreferenceresolution.constructfromhorizon(); ispatialreferencetolerance spatialreferencetolerance = spatialreferenceresolution as ispatialreferencetolerance; ispatialreferencetolerance spatialreferencetolerance = spatialreferenceresolution as ispatialreferencetolerance; spatialreferencetolerance.setdefaultxytolerance(); spatialreferencetolerance.setdefaultxytolerance(); ispatialreference spatialreference = spatialreferenceresolution as ispatialreference; ispatialreference spatialreference = spatialreferenceresolution as ispatialreference;  //create an array of wkspoint structures starting in the middle of the x,y domain of the //create an array of wkspoint structures starting in the middle of the x,y domain of the  //projected coordinate system. //projected coordinate system.  double xmin; double xmin; double xmax; double xmax;  double ymin; double ymin; double ymax; double ymax; spatialreference.getdomain(out xmin, out xmax, out ymin, out ymax); spatialreference.getdomain(out xmin, out xmax, out ymin, out ymax);  double xfactor = (xmin + xmax) * 0.5; double xfactor = (xmin + xmax) * 0.5;  double yfactor = (ymin + ymax) * 0.5; double yfactor = (ymin + ymax) * 0.5;  wkspoint[] wkspoints = new wkspoint[10]; wkspoint[] wkspoints = new wkspoint[10]; for (int i = 0; i < wkspoints.length; i++) for (int i = 0; i < wkspoints.length; i++)    { {  wkspoints[i].x = xfactor + i; wkspoints[i].x = xfactor + i; wkspoints[i].y = yfactor + i; wkspoints[i].y = yfactor + i; } }  ipointcollection4 pointcollection = new polylineclass(); ipointcollection4 pointcollection = new polylineclass();   igeometrybridge2 geometrybridge = new geometryenvironmentclass(); igeometrybridge2 geometrybridge = new geometryenvironmentclass(); geometrybridge.addwkspoints(pointcollection, ref wkspoints); geometrybridge.addwkspoints(pointcollection, ref wkspoints);  ipolyline polyline = pointcollection as ipolyline; ipolyline polyline = pointcollection as ipolyline; polyline.spatialreference = spatialreference; polyline.spatialreference = spatialreference;   return polyline; return polyline; } } |
new geometryenvironmentclass仅仅是创建了一个指向已存在的geometryenvironmentclass的引用。注意 igeometrybridge2接口的使用,addwkspoints方法将wkspoint二维点添加到pointcollection中,用于构建 path、ring、polyline、polygon,或增加新点到multipoint、trianglefan、trianglestrip。在 geometry库中,除了igeometrybridge2还有igeometrybridge接口,后者继承了前者,增加了一些编辑功能(添加点、插入点、重置点、分段等)。
geometrybag
geometrybag是支持igeometry接口的几何对象引用的集合,任何几何对象都可以通过igeometrycollection接口添加到 geometrybag中,但是在使用拓扑操作的时候,需要注意不同类型的几何类型可能会有相互不兼容的情况。在向geometrybag中添加几何对象的时候,geometrybag对象需要指定空间参考,添加到其中的几何对象均拥有和geometrybag对象一样的空间参考。
以下为引用的内容: private ipolygon geometrybag_example(ifeatureclass featureclass) private ipolygon geometrybag_example(ifeatureclass featureclass)   { {   //check input objects. //check input objects. if (featureclass == null) if (featureclass == null)   { {  return null; return null; } }  igeodataset geodataset = featureclass as igeodataset; igeodataset geodataset = featureclass as igeodataset; ispatialfilter queryfilter = new spatialfilterclass(); ispatialfilter queryfilter = new spatialfilterclass();   //set the properties of the spatial filter here. //set the properties of the spatial filter here. igeometry geometrybag = new geometrybagclass(); igeometry geometrybag = new geometrybagclass();  //define the spatial reference of the bag before adding geometries to it. //define the spatial reference of the bag before adding geometries to it.  geometrybag.spatialreference = geodataset.spatialreference; geometrybag.spatialreference = geodataset.spatialreference;  //use a nonrecycling cursor so each returned geometry is a separate object. //use a nonrecycling cursor so each returned geometry is a separate object.  ifeaturecursor featurecursor = featureclass.search(queryfilter, false); ifeaturecursor featurecursor = featureclass.search(queryfilter, false);   igeometrycollection geometrycollection = geometrybag as igeometrycollection; igeometrycollection geometrycollection = geometrybag as igeometrycollection; ifeature currentfeature = featurecursor.nextfeature(); ifeature currentfeature = featurecursor.nextfeature();  while (currentfeature != null) while (currentfeature != null)    { {  //add a reference to this feature's geometry into the bag. //add a reference to this feature's geometry into the bag. //you don't specify the before or after geometry (missing), //you don't specify the before or after geometry (missing), //so the currentfeature.shape igeometry is added to the end of the geometrycollection. //so the currentfeature.shape igeometry is added to the end of the geometrycollection. object missing = type.missing; object missing = type.missing;  geometrycollection.addgeometry(currentfeature.shape, ref missing, ref missing); geometrycollection.addgeometry(currentfeature.shape, ref missing, ref missing);  currentfeature = featurecursor.nextfeature(); currentfeature = featurecursor.nextfeature(); } }  // create the polygon that will be the union of the features returned from the search cursor. // create the polygon that will be the union of the features returned from the search cursor.  // the spatial reference of this feature does not need to be set ahead of time. the // the spatial reference of this feature does not need to be set ahead of time. the  // constructunion method defines the constructed polygon's spatial reference to be the same as // constructunion method defines the constructed polygon's spatial reference to be the same as  // the input geometry bag. // the input geometry bag. itopologicaloperator unionedpolygon = new polygonclass(); itopologicaloperator unionedpolygon = new polygonclass();  unionedpolygon.constructunion(geometrybag as ienumgeometry); unionedpolygon.constructunion(geometrybag as ienumgeometry);  return unionedpolygon as ipolygon; return unionedpolygon as ipolygon;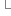 } } |
points
一个点包括x、y坐标,同时可以增加m、z值及id属性来扩展点的功能。
multipoints
点的集合,多点组成multipoint几何类型,使用multipoint对象实现了的ipointcollection接口可以访问所有的点元素,这些点同样可以拥有m、z值及id属性来获得更多的地理空间内涵。
下面列举一个例子,通过一个已知的polyline来定义一个新的multipart polyline。
以下为引用的内容: public ipolyline constructmultipartpolyline(ipolyline inputpolyline) public ipolyline constructmultipartpolyline(ipolyline inputpolyline)   { {  igeometry outgeometry = new polylineclass(); igeometry outgeometry = new polylineclass();  //always associate new, top-level geometries with an appropriate spatial reference. //always associate new, top-level geometries with an appropriate spatial reference. outgeometry.spatialreference = inputpolyline.spatialreference; outgeometry.spatialreference = inputpolyline.spatialreference;   igeometrycollection geometrycollection = outgeometry as igeometrycollection; igeometrycollection geometrycollection = outgeometry as igeometrycollection;  isegmentcollection segmentcollection = inputpolyline as isegmentcollection; isegmentcollection segmentcollection = inputpolyline as isegmentcollection;  //iterate over existing polyline segments using a segment enumerator. //iterate over existing polyline segments using a segment enumerator.  ienumsegment segments = segmentcollection.enumsegments; ienumsegment segments = segmentcollection.enumsegments;  isegment currentsegment; isegment currentsegment; int partindex = 0;; int partindex = 0;; int segmentindex = 0;; int segmentindex = 0;;  segments.next(out currentsegment,ref partindex, ref segmentindex); segments.next(out currentsegment,ref partindex, ref segmentindex); while(currentsegment != null) while(currentsegment != null)   { {  iline normal = new lineclass(); iline normal = new lineclass();  //geometry methods with _query_ in their name expect to modify existing geometries. //geometry methods with _query_ in their name expect to modify existing geometries.  //in this case, the querynormal method modifies an existing line //in this case, the querynormal method modifies an existing line //segment (normal) to be the normal vector to //segment (normal) to be the normal vector to  //currentsegment at the specified location along currentsegment. //currentsegment at the specified location along currentsegment. currentsegment.querynormal(esrisegmentextension.esrinoextension, 0.5, true, currentsegment.length / 3, normal); currentsegment.querynormal(esrisegmentextension.esrinoextension, 0.5, true, currentsegment.length / 3, normal);   //since each normal vector is not connected to others, create a new path for each one. //since each normal vector is not connected to others, create a new path for each one.  isegmentcollection newpath = new pathclass(); isegmentcollection newpath = new pathclass(); object missing = type.missing; object missing = type.missing; newpath.addsegment(normal as isegment, ref missing, ref missing); newpath.addsegment(normal as isegment, ref missing, ref missing);  //the spatial reference associated with geometrycollection will be assigned to all incoming paths and segments. //the spatial reference associated with geometrycollection will be assigned to all incoming paths and segments. geometrycollection.addgeometry(newpath as igeometry, ref missing, ref missing); geometrycollection.addgeometry(newpath as igeometry, ref missing, ref missing);  segments.next(out currentsegment,ref partindex, ref segmentindex); segments.next(out currentsegment,ref partindex, ref segmentindex);  } } //the geometrycollection now contains the new, multipart polyline. //the geometrycollection now contains the new, multipart polyline. return geometrycollection as ipolyline; return geometrycollection as ipolyline; } } |
isegment接口的querynormal方法用来在弧段上的某一点生成该弧段的法线,指定其长度,这样就生成了新的segment,并且多个path添加到geometrycollection中,以ipolyline的形式返回。
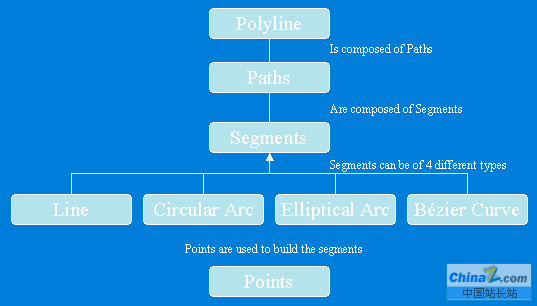
polylines
polylines是有序path组成的集合,可以拥有m、z和id属性值。polyline对象的ipointcollection接口包含了所有节点的复制,igeometrycollection接口可以获取polyline的paths,isegmentcollection接口可以获取 polyline的segments。
polyline结构图
polygons
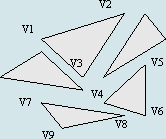
polygon是一系列rings组成的集合,可以拥有m、z和id属性值。每一个ring由一个或多个segment组成,polygon或ring对象的ipointcollection接口包含了所有节点的复制,igeometrycollection接口可以获取polygon的rings, isegmentcollection接口可以获取polygon的segments。
polygon结构图

multipatch
multipatch用于描述3d面状几何类型,由一系列的矢量三角形构成,如果其中的part是一个ring,那么它必须是封闭的,第一个节点和最后一个节点相同,另外每个part所包含节点的顺序非常重要,inner rings在outer rings之后,代表单个表面patch的一系列rings必须由第一个ring开始。
在9.0以后的开发包中,使用igeneralmultipatchcreator创建新的multipatch,igeometrymaterial进行材质贴图。
以下为引用的内容: public imultipatch createmultipatch() public imultipatch createmultipatch()   { {  //prepare the geometry material list. //prepare the geometry material list. igeometrymaterial texture = new geometrymaterialclass(); igeometrymaterial texture = new geometrymaterialclass(); texture.textureimage = "c://temp//myimage.bmp"; texture.textureimage = "c://temp//myimage.bmp";  igeometrymateriallist materiallist = new geometrymateriallistclass(); igeometrymateriallist materiallist = new geometrymateriallistclass(); materiallist.addmaterial(texture); materiallist.addmaterial(texture);  //create the multipatch. //create the multipatch. igeneralmultipatchcreator multipatchcreator = new generalmultipatchcreatorclass(); igeneralmultipatchcreator multipatchcreator = new generalmultipatchcreatorclass();  multipatchcreator.init(4, 1, false, false, false, 4, materiallist); multipatchcreator.init(4, 1, false, false, false, 4, materiallist);  //set up part. //set up part.  //could also use a ring or a trianglefan. //could also use a ring or a trianglefan.  multipatchcreator.setpatchtype(0, esripatchtype.esripatchtypetrianglestrip); multipatchcreator.setpatchtype(0, esripatchtype.esripatchtypetrianglestrip); multipatchcreator.setmaterialindex(0, 0); multipatchcreator.setmaterialindex(0, 0); multipatchcreator.setpatchpointindex(0, 0); multipatchcreator.setpatchpointindex(0, 0); multipatchcreator.setpatchtexturepointindex(0, 0); multipatchcreator.setpatchtexturepointindex(0, 0);   //set real-world points. //set real-world points. wkspointz upperleft = new wkspointz(); wkspointz upperleft = new wkspointz(); wkspointz lowerleft = new wkspointz(); wkspointz lowerleft = new wkspointz(); wkspointz upperright = new wkspointz(); wkspointz upperright = new wkspointz();  wkspointz lowerright = new wkspointz(); wkspointz lowerright = new wkspointz();  upperleft.x = 0; upperleft.x = 0; upperleft.y = 0; upperleft.y = 0; upperleft.z = 0; upperleft.z = 0;  upperright.x = 300; upperright.x = 300; upperright.y = 0; upperright.y = 0; upperright.z = 0; upperright.z = 0; lowerleft.x = 0; lowerleft.x = 0;  lowerleft.y = 0; lowerleft.y = 0; lowerleft.z = -100; lowerleft.z = -100; lowerright.x = 300; lowerright.x = 300; lowerright.y = 1; lowerright.y = 1;  lowerright.z = -100; lowerright.z = -100;  multipatchcreator.setwkspointz(0, ref upperright); multipatchcreator.setwkspointz(0, ref upperright); multipatchcreator.setwkspointz(1, ref lowerright); multipatchcreator.setwkspointz(1, ref lowerright); multipatchcreator.setwkspointz(2, ref upperleft); multipatchcreator.setwkspointz(2, ref upperleft);  multipatchcreator.setwkspointz(3, ref lowerleft); multipatchcreator.setwkspointz(3, ref lowerleft);  //set texture points. //set texture points. //set the texture coordinates for a panel. //set the texture coordinates for a panel. wkspoint textureupperleft = new wkspoint(); wkspoint textureupperleft = new wkspoint();  wkspoint texturelowerleft = new wkspoint(); wkspoint texturelowerleft = new wkspoint(); wkspoint textureupperright = new wkspoint(); wkspoint textureupperright = new wkspoint(); wkspoint texturelowerright = new wkspoint(); wkspoint texturelowerright = new wkspoint();  textureupperleft.x = 0; textureupperleft.x = 0;  textureupperleft.y = 0; textureupperleft.y = 0; textureupperright.x = 1; textureupperright.x = 1; textureupperright.y = 0; textureupperright.y = 0; texturelowerleft.x = 0; texturelowerleft.x = 0;  texturelowerleft.y = 1; texturelowerleft.y = 1; texturelowerright.x = 1; texturelowerright.x = 1; texturelowerright.y = 1; texturelowerright.y = 1;  multipatchcreator.settexturewkspoint(0, ref textureupperright); multipatchcreator.settexturewkspoint(0, ref textureupperright);  multipatchcreator.settexturewkspoint(1, ref texturelowerright); multipatchcreator.settexturewkspoint(1, ref texturelowerright); multipatchcreator.settexturewkspoint(2, ref textureupperleft); multipatchcreator.settexturewkspoint(2, ref textureupperleft); multipatchcreator.settexturewkspoint(3, ref texturelowerleft); multipatchcreator.settexturewkspoint(3, ref texturelowerleft); imultipatch multipatch = multipatchcreator.createmultipatch() as imultipatch; imultipatch multipatch = multipatchcreator.createmultipatch() as imultipatch;   return multipatch; return multipatch; } } |
新闻热点
疑难解答