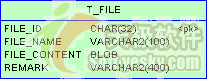
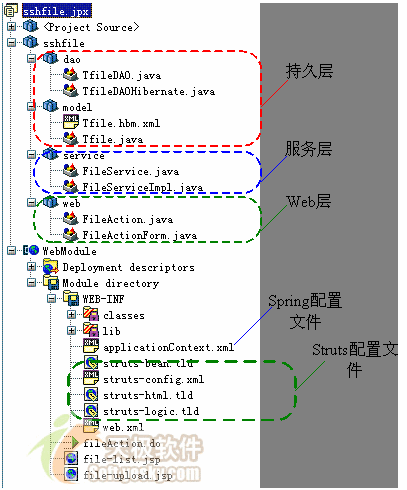
工程的类按ssh的层次结构划分为数据持久层、业务层和web层;web-inf下的applicationcontext.xml为spring的配置文件,struts-config.xml为struts的配置文件,file-upload.jsp为文件上传页面,file-list.jsp为文件列表页面。
本文后面的章节将从数据持久层->业务层->web层的开发顺序,逐层讲解文件上传下载的开发过程。
数据持久层
1、领域对象及映射文件
您可以使用hibernate middlegen、hibernate tools、hibernate syhchronizer等工具或手工的方式,编写hibernate的领域对象和映射文件。其中对应t_file表的领域对象tfile.java为:
代码 1 领域对象tfile
1. package sshfile.model;
2. public class tfile
3.{
4. private string fileid;
5. private string filename;
6. private byte[] filecontent;
7. private string remark;
8. …//getter and setter
9. }
1. <?xml version="1.0"?>
2. <!doctype hibernate-mapping public
3. "-//hibernate/hibernate mapping dtd 3.0//en"
4. "http://hibernate.sourceforge.net/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd" >
5. <hibernate-mapping>
6. <class name="sshfile.model.tfile" table="t_file">
7. <id name="fileid" type="java.lang.string" column="file_id">
8. <generator class="uuid.hex"/>
9. </id>
10. <property name="filecontent"
11. type="org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.support.blobbytearraytype"
12. column="file_content" lazy="true"/>
13. …//其它一般字段的映射
14. </class>
15. </hibernate-mapping>
1. package sshfile.dao;
2.
3. import sshfile.model.*;
4. import org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.support.hibernatedaosupport;
5. import java.util.list;
6.
7. public class tfiledaohibernate
8. extends hibernatedaosupport implements tfiledao
9. {
10. public tfile findbyfildid(string fileid)
11. {
12. return (tfile) gethibernatetemplate().get(tfile.class, fileid);
13. }
14. public void save(tfile tfile)
15. {
16. gethibernatetemplate().save(tfile);
17. gethibernatetemplate().flush();
18. }
19. public list findall()
20. {
21. return gethibernatetemplate().loadall(tfile.class);
22. }
23. }
1. <beans>
2. <!-- 数据源的配置 //-->
3. <bean id="datasource" class="org.apache.commons.dbcp.basicdatasource"
4. destroy-method="close">
5. <property name="driverclassname" value="oracle.jdbc.driver.oracledriver"/>
6. <property name="url" value="jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:ora9i"/>
7. <property name="username" value="test"/>
8. <property name="password" value="test"/>
9. </bean>
10. <!-- hibernate会话工厂配置 //-->
11. <bean id="sessionfactory"
12. class="org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.localsessionfactorybean">
13. <property name="datasource" ref="datasource"/>
14. <property name="mappingdirectorylocations">
15. <list>
16. <value>classpath:/sshfile/model</value>
17. </list>
18. </property>
19. <property name="hibernateproperties">
20. <props>
21. <prop key="hibernate.dialect">org.hibernate.dialect.oracledialect</prop>
22. <prop key="hibernate.cglib.use_reflection_optimizer">true</prop>
23. </props>
24. </property>
25. </bean>
26. <!-- hibernate 模板//-->
27. <bean id="hibernatetemplate"
28. class="org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.hibernatetemplate">
29. <property name="sessionfactory" ref="sessionfactory"/>
30. </bean>
31. <!--dao配置 //-->
32. <bean id="tfiledao" class="sshfile.dao.tfiledaohibernate">
33. <property name="hibernatetemplate" ref="hibernatetemplate" />
34. </bean>
35. …
36. </beans>
1. <beans>
2. …
3. <bean id="nativejdbcextractor"
4. class="org.springframework.jdbc.support.nativejdbc.commonsdbcpnativejdbcextractor"
5. lazy-init="true"/>
6. <bean id="lobhandler"
7. class="org.springframework.jdbc.support.lob.oraclelobhandler" lazy-init="true">
8. <property name="nativejdbcextractor">
9. <ref local="nativejdbcextractor"/>
10. </property>
11. </bean>
12. …
13. </beans>
1. <beans>
2. …
3. <bean id="sessionfactory"
4. class="org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.localsessionfactorybean">
5. <property name="datasource" ref="datasource"/>
6. <!-- 为处理blob类型字段的句柄声明 //-->
7. <property name="lobhandler" ref="lobhandler"/>
8. …
9. </bean>
10. …
11. </beans>
业务层
1、业务层接口
"面向接口而非面向类编程"是spring不遗余力所推荐的编程原则,这条原则也已经为大部开发者所接受;此外,jdk的动态代理只对接口有效,否则必须使用cglib生成目标类的子类。我们依从于spring的倡导为业务类定义一个接口:
代码 7 业务层操作接口
1. public interface fileservice
2. {
3. void save(fileactionform fileform);//将提交的上传文件保存到数据表中
4. list getallfile();//得到t_file所示记录
5. void write(outputstream os,string fileid);//将某个文件的文件数据写出到输出流中
6. string getfilename(string fileid);//获取文件名
7. }
1. …
2. public class fileserviceimpl
3. implements fileservice
4. {
5. private tfiledao tfiledao;
6. public void save(fileactionform fileform)
7. {
8. tfile tfile = new tfile();
9. try
10. {
11. tfile.setfilecontent(fileform.getfilecontent().getfiledata());
12. }
13. catch (filenotfoundexception ex)
14. {
15. throw new runtimeexception(ex);
16. }
17. catch (ioexception ex)
18. {
19. throw new runtimeexception(ex);
20. }
21. tfile.setfilename(fileform.getfilecontent().getfilename());
22. tfile.setremark(fileform.getremark());
23. tfiledao.save(tfile);
24. }
25. …
26. }
1. …
2. public class fileserviceimpl
3. implements fileservice
4. {
5.
6. public void write(outputstream os, string fileid)
7. {
8. tfile tfile = tfiledao.findbyfildid(fileid);
9. try
10. {
11. os.write(tfile.getfilecontent());
12. os.flush();
13. }
14. catch (ioexception ex)
15. {
16. throw new runtimeexception(ex);
17. }
18. }
19. …
20. }
1. <beans>
2. …
3. <bean id="transactionmanager"
4. class="org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.hibernatetransactionmanager">
5. <property name="sessionfactory" ref="sessionfactory"/>
6. </bean>
7. <!-- 事务处理的aop配置 //-->
8. <bean id="txproxytemplate" abstract="true"
9. class="org.springframework.transaction.interceptor.transactionproxyfactorybean">
10. <property name="transactionmanager" ref="transactionmanager"/>
11. <property name="transactionattributes">
12. <props>
13. <prop key="get*">propagation_required,readonly</prop>
14. <prop key="find*">propagation_required,readonly</prop>
15. <prop key="save">propagation_required</prop>
16. <prop key="write">propagation_required,readonly</prop>
17. </props>
18. </property>
19. </bean>
20. <bean id="fileservice" parent="txproxytemplate">
21. <property name="target">
22. <bean class="sshfile.service.fileserviceimpl">
23. <property name="tfiledao" ref="tfiledao"/>
24. </bean>
25. </property>
26. </bean>
27. </beans>
web层实现
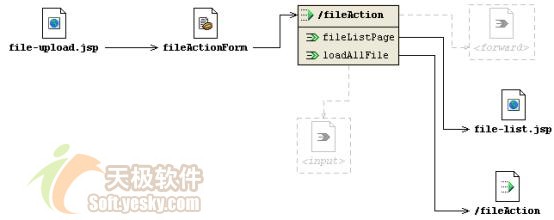
1、web层的构件和交互流程
web层包括主要3个功能:
·上传文件。
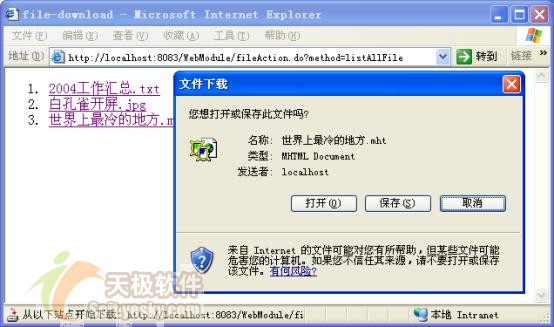
·列出所有已经上传的文件列表,以供点击下载。
·下载文件。
web层实现构件包括与2个jsp页面,1个actionform及一个action:
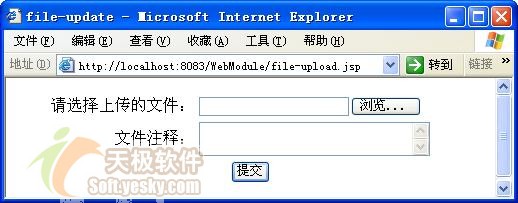
·file-upload.jsp:上传文件的页面。
·file-list.jsp:已经上传文件的列表页面。
·fileactionform:file-upload.jsp页面表单对应的actionform。
·fileaction:继承org.apache.struts.actions.dispatchaction的action,这样这个action就可以通过一个url参数区分中响应不同的请求。
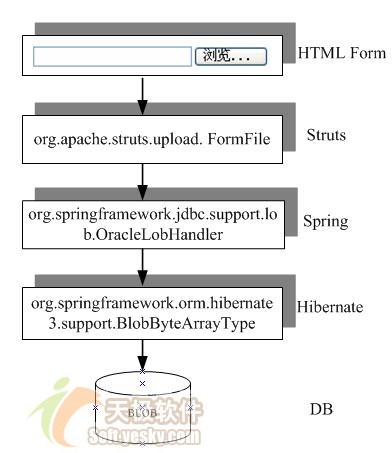
web层的这些构件的交互流程如图 6所示:
1. <struts-config>
2. <form-beans>
3. <form-bean name="fileactionform" type="sshfile.web.fileactionform" />
4. </form-beans>
5. <action-mappings>
6. <action name="fileactionform" parameter="method" path="/fileaction"
7. type="sshfile.web.fileaction">
8. <forward name="filelistpage" path="/file-list.jsp" />
9. <forward name="loadallfile" path="/fileaction.do?method=listallfile" />
10. </action>
11. </action-mappings>
12. </struts-config>
1. public class fileaction
2. extends dispatchaction
3. {
4. //将上传文件保存到数据库中
5. public actionforward upload(actionmapping mapping, actionform form,
6. httpservletrequest request,
7. httpservletresponse response)
8. {
9. fileactionform fileform = (fileactionform) form;
10. fileservice fileservice = getfileservice();
11. fileservice.save(fileform);
12. return mapping.findforward("loadallfile");
13. }
14. //从spring容器中获取fileservice对象
15. private fileservice getfileservice()
16. {
17. applicationcontext appcontext = webapplicationcontextutils.
18. getwebapplicationcontext(this.getservlet().getservletcontext());
19. return (fileservice) appcontext.getbean("fileservice");
20. }
21. …
22. }
1. public class fileaction
2. extends dispatchaction
3. {
4. …
5. public actionforward listallfile(actionmapping mapping, actionform form,
6. httpservletrequest request,
7. httpservletresponse response)
8. throws moduleexception
9. {
10. fileservice fileservice = getfileservice();
11. list filelist = fileservice.getallfile();
12. request.setattribute("filelist",filelist);
13. return mapping.findforward("filelistpage");
14. }
15. }
1. <%@page contenttype="text/html; charset=gbk"%>
2. <%@taglib uri="/web-inf/struts-logic.tld" prefix="logic"%>
3. <%@taglib uri="/web-inf/struts-bean.tld" prefix="bean"%>
4. <html>
5. <head>
6. <title>file-download</title>
7. </head>
8. <body bgcolor="#ffffff">
9. <ol>
10. <logic:iterate id="item" name="filelist" scope="request">
11. <li>
12. <a href='fileaction.do?method=download&fileid=
13. <bean:write name="item"property="fileid"/>'>
14. <bean:write name="item" property="filename"/>
15. </a>
16. </li>
17. </logic:iterate>
18. </ol>
19. </body>
20. </html>

1. public class fileaction
2. extends dispatchaction
3. {
4. …
5. public actionforward download(actionmapping mapping, actionform form,
6. httpservletrequest request,
7. httpservletresponse response)
8. throws moduleexception
9. {
10. fileactionform fileform = (fileactionform) form;
11. fileservice fileservice = getfileservice();
12. string filename = fileservice.getfilename(fileform.getfileid());
13. try
14. {
15. response.setcontenttype("application/x-msdownload");
16. response.setheader("content-disposition",
17. "attachment;" + " filename="+
18. new string(filename.getbytes(), "iso-8859-1"));
19. fileservice.write(response.getoutputstream(), fileform.getfileid());
20. }
21. catch (exception e)
22. {
23. throw new moduleexception(e.getmessage());
24. }
25. return null;
26. }
27. }
1. <web-app>
2. <context-param>
3. <param-name>contextconfiglocation</param-name>
4. <param-value>/web-inf/applicationcontext.xml</param-value>
5. </context-param>
6. <context-param>
7. <param-name>log4jconfiglocation</param-name>
8. <param-value>/web-inf/log4j.properties</param-value>
9. </context-param>
10. <servlet>
11. <servlet-name>log4jinitservlet</servlet-name>
12. <servlet-class>org.springframework.web.util.log4jconfigservlet</servlet-class>
13. <load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
14. </servlet>
15. <servlet>
16. <servlet-name>springinitservlet</servlet-name>
17. <servlet-class>org.springframework.web.context.contextloaderservlet</servlet-class>
18. <load-on-startup>2</load-on-startup>
19. </servlet>
20. …
21. </web-app>
1. <web-app>
2. …
3. <filter>
4. <filter-name>encodingfilter</filter-name>
5. <filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.characterencodingfilter</filter-class>
6. <init-param>
7. <param-name>encoding</param-name>
8. <param-value>gbk</param-value>
9. </init-param>
10. </filter>
11. <filter-mapping>
12. <filter-name>encodingfilter</filter-name>
13. <url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
14. </filter-mapping>
15. …
16. </web-app>
新闻热点
疑难解答