作为这个介绍spring框架中的面向方面编程(aspect-oriented programming,aop)的系列的第一部分,本文介绍了使您可以使用spring中的面向方面特性进行快速开发的基础知识。使用跟踪和记录方面(面向方面领域的helloworld)作为例子,本文展示了如何使用spring框架所独有的特性来声明切入点和通知以便应用方面。本系列的第二部分将更深入地介绍如何运用spring中的所有通知类型和切入点来实现更实用的方面和面向方面设计模式。
public interface ibusinesslogic
{
public void foo();
}
public class businesslogic
implements ibusinesslogic
{
public void foo()
{
system.out.println("inside businesslogic.foo()");
}
}
import org.springframework.context.applicationcontext;
import org.springframework.context.support.filesystemxmlapplicationcontext;
public class mainapplication
{
public static void main(string [] args)
{
// read the configuration file
applicationcontext ctx = new filesystemxmlapplicationcontext("springconfig.xml");
//instantiate an object
ibusinesslogic testobject = (ibusinesslogic) ctx.getbean("businesslogicbean");
// execute the public
// method of the bean
testobject.foo();
}
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<!doctype beans public
"-//spring//dtd bean//en"
"http://www.springframework.org/dtd/spring-beans.dtd">
<beans>
<!-- bean configuration -->
<bean id="businesslogicbean"
class="org.springframework.aop.framework.proxyfactorybean">
<property name="proxyinterfaces">
<value>ibusinesslogic</value>
</property>
<property name="target">
<ref local="beantarget"/>
</property>
</bean>
<!-- bean classes -->
<bean id="beantarget"
class="businesslogic"/>
</beans>

import java.lang.reflect.method;
import org.springframework.aop. methodbeforeadvice;
public class tracingbeforeadvice
implements methodbeforeadvice
{
public void before(method m, object[] args, object target)
throws throwable
{
system.out.println("hello world! (by " + this.getclass().getname() + ")");
}
}
import java.lang.reflect.method;
import org.springframework.aop.afterreturningadvice;
public class tracingafteradvice
implements afterreturningadvice
{
public void afterreturning(object object, method m, object[] args, object target)
throws throwable
{
system.out.println("hello world! (by " + this.getclass().getname() + ")");
}
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<!doctype beans public
"-//spring//dtd bean//en"
"http://www.springframework.org/dtd/spring-beans.dtd">
<beans>
<!-- bean configuration -->
<bean id="businesslogicbean"
class="org.springframework.aop.framework.proxyfactorybean">
<property name="proxyinterfaces">
<value>ibusinesslogic</value>
</property>
<property name="target">
<ref local="beantarget"/>
</property>
<property name="interceptornames">
<list>
<value>thetracingbeforeadvisor</value>
<value>thetracingafteradvisor</value>
</list>
</property>
</bean>
<!-- bean classes -->
<bean id="beantarget"
class="businesslogic"/>
<!-- advisor pointcut definition for before advice -->
<bean id="thetracingbeforeadvisor"
class="org.springframework.aop.support.regexpmethodpointcutadvisor">
<property name="advice">
<ref local="thetracingbeforeadvice"/>
</property>
<property name="pattern">
<value>.*</value>
</property>
</bean>
<!-- advisor pointcut definition for after advice -->
<bean id="thetracingafteradvisor"
class="org.springframework.aop.support.regexpmethodpointcutadvisor">
<property name="advice">
<ref local="thetracingafteradvice"/>
</property>
<property name="pattern">
<value>.*</value>
</property>
</bean<
<!-- advice classes -->
<bean id="thetracingbeforeadvice"
class="tracingbeforeadvice"/>
<bean id="thetracingafteradvice"
class="tracingafteradvice"/>
</beans>
<value>.*</value>:该表达式选择advisor所关联到的一个或多个bean上的所有联结点。
<value>./ibusinesslogic/.foo</value>:该表达式只选择ibusinesslogic接口上的foo()方法的联结点。如果是advisor所关联到的bean,则该表达式只选择ibusinesslogic接口上的联结点。
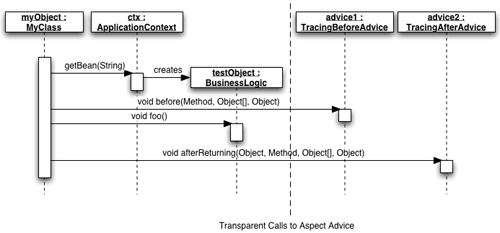
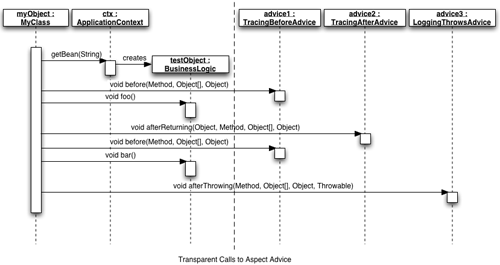
方法跟踪方面和例子应用程序的源代码可在本文末尾的参考资料小节进行下载。
方面的重用
可以对方法跟踪方面进行扩展,提供一个稍微复杂的记录(logging)方面。记录方面提供了一个很不错的重用例子,因为记录方面所需的许多特性都已经包含在方法跟踪方面中了。
在本例中,记录方面扩展了方法跟踪方面,以便显示附加的与(在应用程序的执行过程中)所引发的异常有关的信息。
要完全使用记录方面,需要对应用程序做一些更改。businesslogicexception异常类提供了一个可以由ibusinesslogicinterface接口和businesslogic实现类新增的void bar()方法引发的异常。
public class businesslogicexception
extends exception
{}
public interface ibusinesslogic
{
public void foo();
public void bar()
throws businesslogicexception;
}
public class businesslogic
implements ibusinesslogic
{
public void foo()
{
system.out.println("inside businesslogic.foo()");
}
public void bar()
throws businesslogicexception
{
system.out.println("inside businesslogic.bar()");
throw new businesslogicexception();
}
}
import org.springframeworkcontext.applicationcontext;
import org.springframework.context.support.filesystemxmlapplicationcontext;
public class mainapplication
{
public static void main(string [] args)
{
// read the configuration file
applicationcontext ctx = new filesystemxmlapplicationcontext( "springconfig.xml");
//instantiate an object
ibusinesslogic testobject = (ibusinesslogic) ctx.getbean("businesslogicbean");
//execute the public methods of the bean
testobject.foo();
try
{
testobject.bar();
}
catch(businesslogicexception ble)
{
system.out.println("caught businesslogicexception");
}
}
}
import org.springframework.aop.throwsadvice;
import java.lang.reflect.method;
public class loggingthrowsadvice
implements throwsadvice
{
public void afterthrowing(method method, object[] args, object target, throwable subclass)
{
system.out.println("logging that a " + subclass + "exception was thrown.");
}
}
新闻热点
疑难解答