<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?> <?eclipse version="3.0"?> <plugin id="org.eclipse.draw2d" name="draw2d" version="3.0.0" provider-name="eclipse.org"> <runtime> <library name="draw2d.jar"> <export name="*" /> <packages prefixes="org.eclipse.draw2d" /> </library> </runtime> <requires> <import plugin="org.eclipse.swt" export="true" /> <import plugin="org.eclipse.core.runtime" /> </requires> </plugin>
程序员通常会将第二个地方称为 links 文件夹。这个 links 文件夹中包含 0 个或多个文件,文件名通常都是以 “.link” 扩展名结尾。这些文件中包含了一些链接信息,可以使用这些信息定位在磁盘上哪些地方可以找到链接插件。
每个 .link 文件都有一个关键字-值对,其格式为 path=location。(例如,links 文件夹 c:/eclipse/links 中就可能会有很多 .link 文件,其中一个文件的名字可能为 com.ibm.indiver.dependencywalker.link。这个文件中唯一的一行可能类似于 path=c:/myplugins/dependencywalker)。这个 .link 文件会将 eclipse 引导到指定的位置,并在 /eclipse/plugins 文件夹中寻找更多的可用插件。
创建自己的 eclipse 插件依赖性遍历程序
编写一个依赖性遍历程序基本上分为两个步骤:首先罗列出所有插件,其次罗列出用户所选择的插件的依赖性。
第一个步骤要负责定位 eclipse 系统中出现的每个插件,并在一个简单的用户界面(ui)—— 例如表 —— 中为终端用户提供所有插件的清单。这个 ui 还应该为用户提供一些方法来选择希望解析其依赖性的插件。
第二个步骤则要对用户选择的插件的 plugin.xml 文件进行分析,并查找这个 plugin.xml 文件中嵌入的 <import plugin="plugin id"/> 声明。这种努力显然需要对每个插件的 manifest 文件进行递归搜索,从而查明依赖插件的整个链条。对于描述这个插件可能依赖于其他插件的父-兄-子关系,树状视图是最合适的一种 ui。我们还应该可以直观地看出某个 eclipse 插件注册项是否真正加载了一个物理存在的插件。
步骤 1:罗列 eclipse 系统中的所有插件
在掌握了以下信息之后,就可以编写一些代码来罗列磁盘上物理存在的所有插件了:
下面是罗列 eclipse 系统中所有插件的详细步骤:
清单 2. 准备在 eclipse 系统下物理存在的所有插件的清单
/** * * @return returns a vector containing plugindata objects. * each plugindata object represents a plugin found under any of the following * plugin directories * a. the targetplatformlocation/eclipse/plugins directory, * b. other plugin directories as specified by *.link files under * targetplatform/eclipse/links directory **/ public static vector getpluginsintargetplatform(){ /** //step1: get path of target platform. //step2: prepare path of links folder. //step3: get list of files in links folder. //step4: parse each link file and get the path of linked eclipse folder. //step5: prepare a list of all plugin root folders // (eclipse plugins and linked eclipse plugins). //step6: 6a. for each plugin root folder, // 6b. go to each plugin directory and get path of plugin.xml. //step7: parse the plugin.xml file to get plugin id, plugin version, // and store in vectors, lists, etc. //step8: go back to step 6 to continue with next plugin directory. **/ //step1: get path of target platform. //fall back to eclipse install location if targetplatform in not set. url platformurl = platform.getinstalllocation().geturl(); location location = platform.getinstalllocation(); ipath eclipsepath = null ; //get path of target platform against which the users of this tool //will compile their code. ipath targetplatformlocation = new path(gettargetplatformpath(true)); if(_usetargetplatform == false) eclipsepath = new path(platformurl.getpath()); else eclipsepath = targetplatformlocation; showmessage("considering target platform to be: " + eclipsepath.tostring()); //step2: prepare path of links folder. //step3: get list of files in links folder. //step4: parse each link file and get the path of linked eclipse folder. ipath linkspath = new path( eclipsepath.tostring() ).append("/links"); string linkedpaths[] = getlinkedpaths(linkspath.tostring()); int linkedpathlength = 0; if(null != linkedpaths){ linkedpathlength = linkedpaths.length; } //step5: prepare a list of all plugin root folders // (eclipse plugins and linked eclipse plugins). ipath eclipsepluginrootfolders[] = new ipath[linkedpathlength + 1]; eclipsepluginrootfolders[0] = new path( eclipsepath.tostring() ).append("/plugins"); if(null != linkedpaths){ for(int i=0; i<linkedpaths.length; i++){ eclipsepluginrootfolders[i+1] = new path(linkedpaths[i]).append("/eclipse/plugins"); } } //step6: 6a. for each plugin root folder, // 6b. go to each plugin directory and get path of plugin.xml. //step7: parse the plugin.xml file to get plugin id, plugin version, // and store in vectors, lists, etc. vector vectorsinthisvector = new vector(); for(int i=0; i<eclipsepluginrootfolders.length; i++){ system.out.println("/n========plugin ids and versions in " + eclipsepluginrootfolders[i] + "========"); vector plugindataobjs = getplugindataforallplugins( eclipsepluginrootfolders[i].tostring()); vectorsinthisvector.add(plugindataobjs); system.out.println(plugindataobjs); system.out.println("/n===========|||=== end ===|||==========="); } vector plugindata = new vector(); iterator outeriterator = vectorsinthisvector.iterator(); while(outeriterator.hasnext()){ vector plugindataobjs = (vector)outeriterator.next(); iterator inneriterator = plugindataobjs.iterator(); while(inneriterator.hasnext()){ plugindata pd = (plugindata)inneriterator.next(); string pluginidkey = pd.getpluginid(); string versionvalue = pd.getpluginversion(); string pluginpath = pd.getpluginlocation(); plugindata.add(pd); } } int breakpoint=0; return plugindata; } 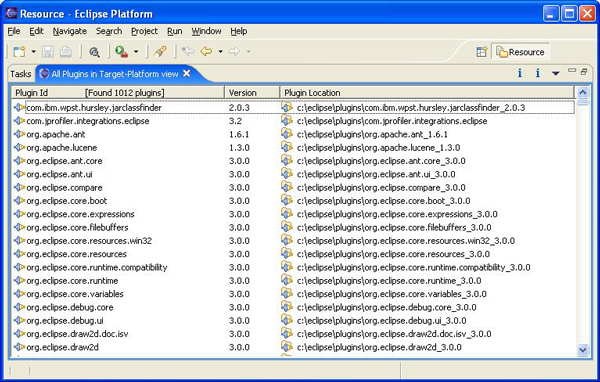
当用户选择希望解析依赖链的插件之后,我们就需要对用户所选择的插件的 plugin.xml 文件进行分析,从而查看它的依赖性。每个依赖性都会导致检查另外一个 plugin.xml 文件,后者又有自己的依赖性。从用户选择的插件开始,这个依赖链可以迅速导致有很多个 plugin.xml 文件需要进行分析。我们可以编写一个递归函数来遍历这些依赖性,它可以查找某个插件的最新版本(针对在相同的系统中有重复插件的情况)以及它的所有依赖性。
编写这种递归函数需要执行的步骤如下所示,清单 3 给出了这个函数的源代码。递归函数有时对资源的消耗量很大,而且在用户失去耐心之前可能还没有返回结果。另外一种选择是编写一个函数,只获取用户选择的插件的直接依赖性清单。后一种方法请参看样例代码中的 loadimmediatedependencies() 函数。
清单 3. recursiveplugindependencywalker() 函数
private vector alreadynotified = new vector(); private boolean firstcall = true; private treeparent root = null; private void recursiveplugindependencywalker(plugindata pdobject, treeparent parentnode){ try { string path = pdobject.getpluginlocation(); pluginparser pp = null; file plugindotxmlfile = new file(path + "/plugin.xml"); if(plugindotxmlfile.exists()){ pp = new pluginparser(plugindotxmlfile); }else{ file fragmentdotxmlfile = new file(path + "/fragment.xml"); if(fragmentdotxmlfile.exists()){ pp = new pluginparser(fragmentdotxmlfile); }else{ return;//no plugin.xml or fragment.xml found } } string displayname = pdobject.getdisplayname(); system.out.println("/nplugin ["+ displayname + "] requires" + "/n"); string requires[] = pp.getdependencylist(); if(0 != requires.length ){ for(int i=0; i<requires.length; i++){ system.out.println("/t" + requires[i] ); plugindata pd[] = getplugindataobjectsfrompluginid(requires[i]); plugindata nextplugin = null; switch(pd.length){ case 0: //great, we know there is //something missing nextplugin = null; break; case 1: //best case, everything will be smooth nextplugin = pd[0]; break; default: //worst case, there must be more //than 1 plugin with the same id //at different locations. string msgline1 = "plugin " + displayname + " requires " + requires[i] + "/n"; string msgline2 = "duplicate plug-ins found for id: / " " + requires[i] + "/"" + "/n continuing with higher version... " ; //it is bad to give repeated //reminders, //so remind only once per plugin id. if(! alreadynotified.contains( new string(requires[i]))){ messagedialog.openinformation(null, "dependency walker", msgline1 + msgline2); alreadynotified.add( new string(requires[i])); } //always take the better //version anyway nextplugin = getbetterversionplugin(pd); break; }//end of switch if( null != nextplugin ){ treeparent nextinline = new treeparent( nextplugin.getdisplayname(), nextplugin.isplugin loadedinregistry() ); parentnode.addchild(nextinline); recursiveplugindependencywalker( nextplugin, nextinline); }else{ treeparent nextinline = new treeparent( requires[i] + " [this plug-in is missing] ", false); parentnode.addchild(nextinline); //obviously we can't recurse //into a missing plugin... } }//end of for }else{ system.out.println("/t nothing: no further dependency /n" ); //no further dependency } } catch (exception e) { e.printstacktrace(); } } 在这种情况中,必须要确定从这两个或更多个磁盘副本中选用哪个插件。显然,我们所感兴趣的应该是最新的插件,也就是说,版本较新的插件。我们可以利用现有的一些函数来对 eclipse 插件的版本进行比较,或者可以基于清单 4 所示的样例代码编写一个简单的函数来对插件版本进行比较。
清单 4. 比较插件版本
private plugindata getbetterversionplugin(plugindata pdo[]){ plugindata _pdobjs[] = pdo; int len = pdo.length; if(len==0) return null; arrays.sort(_pdobjs,new comparator() { /**compares its two arguments for order. * returns a negative integer, zero, or a positive integer * as the first argument is less than, equal to, or greater than * the second. **/ public int compare(object leftobj, object riteobj) { string leftpid = ((plugindata)leftobj). getpluginversion().replace('.', ':'); string ritepid = ((plugindata)riteobj). getpluginversion().replace('.', ':'); string leftid[] = leftpid.split(":"); string riteid[] = ritepid.split(":"); int maxlen = leftid.length > riteid.length ? leftid.length : riteid.length; for(int i=0; i<maxlen; i++){ int left = 0; int rite = 0; try { left = new integer(leftid[i]).intvalue(); } catch (nullpointerexception e) { left = 0; } try { rite = new integer(riteid[i]).intvalue(); } catch (nullpointerexception e) { rite = 0; } if(left==rite){ continue; }else{ int bigger = left > rite ? left : rite; if(bigger==left) return 1; if(bigger==rite) return -1; } } return 0; } public boolean equals(object arg0) { return false; } }); return _pdobjs[len-1]; } 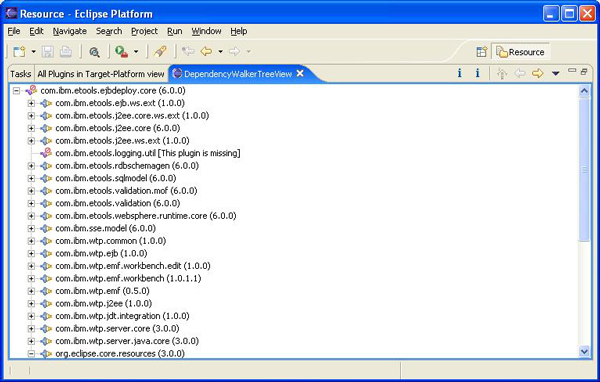
新闻热点
疑难解答