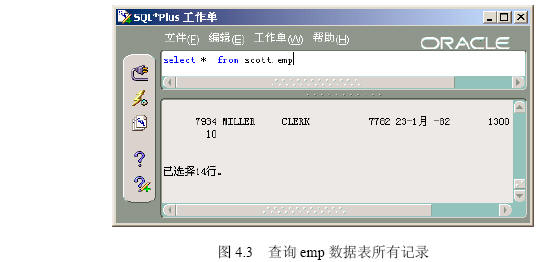
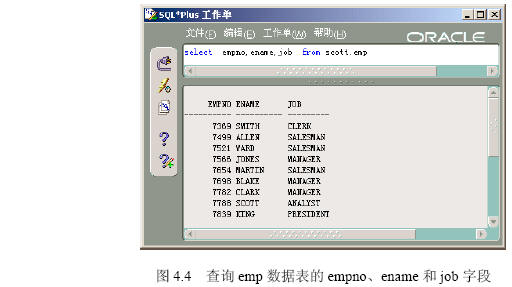
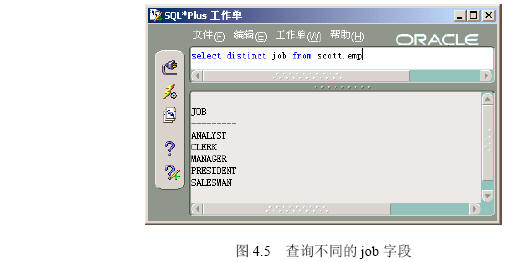

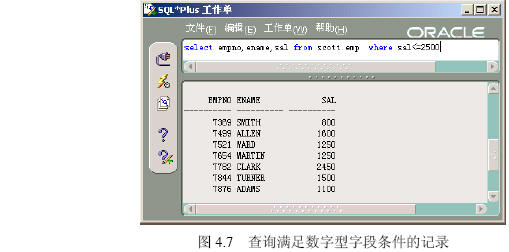
| 名称 | 实例 |
| =(等于) | select * from scott.emp where job=’manager’; |
| select * from scott.emp where sal=1100; | |
| != (不等于) | select * from scott.emp where job!=’manager’; |
| select * from scott.emp where sal!=1100; | |
| ^=(不等于) | select * from scott.emp where job^=’manager’; |
| select * from scott.emp where sal^=1100; | |
| <>(不等于) | select * from scott.emp where job<>’manager’; |
| select * from scott.emp where sal<>1100; | |
| <(小于) | select * from scott.emp where sal<2000; |
| select * from scott.emp where job<’manager’; | |
| >(大于) | select * from scott.emp where sal>2000; |
| select * from scott.emp where job>’manager’; | |
| <=(小于等于) | select * from scott.emp where sal<=2000; |
| select * from scott.emp where job<=’manager’; | |
| >=(大于等于) | select * from scott.emp where sal>=2000; |
| select * from scott.emp where job>=’manager’; | |
| in(列表) | select * from scott.emp where sal in (2000,1000,3000); |
| select * from scott.emp where job in (’manager’,’clerk’); | |
| not in(不在列表) | select * from scott.emp where sal not in (2000,1000,3000); |
| select * from scott.emp where job not in (’manager’,’clerk’); | |
| between(介于之间) | select * from scott.emp where sal between 2000 and 3000; |
| select * from scott.emp where job between ’manager’ and ’clerk’; | |
| not between (不介于之间) | select * from scott.emp where sal not between 2000 and 3000; |
| select * from scott.emp where job not between ’manager’ and ’clerk’; | |
| like(模式匹配) | select * from scott.emp where job like ’m%’; |
| select * from scott.emp where job like ’m__’; | |
| not like (模式不匹配) | select * from scott.emp where job not like ’m%’; |
| select * from scott.emp where job not like ’m__’; | |
| is null (是否为空) | select * from scott.emp where sal is null; |
| select * from scott.emp where job is null; | |
| is not null(是否为空) | select * from scott.emp where sal is not null; |
| select * from scott.emp where job is not null; |
like和not like适合字符型字段的查询,%代表任意长度的字符串,_下划线代表一个任意的字符。like ‘m%’ 代表m开头的任意长度的字符串,like ‘m__’ 代表m开头的长度为3的字符串。
4.2.5 组合条件的查询
(1)在【命令编辑区】输入“select empno,ename,job from scott.emp where job>=’clerk’ and sal<=2000”,然后单击【执行】按钮,出现如图4.8所示的逻辑与组合查询的结果。
【参见光盘文件】:/第4章/4.2/425-1.sql。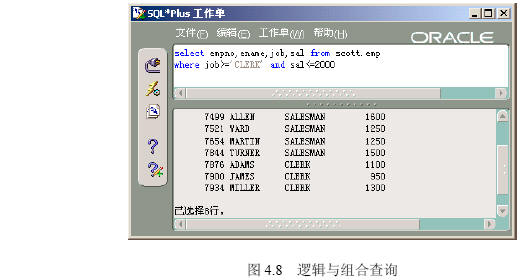
(2)在【命令编辑区】输入“select empno,ename,job from scott.emp where job>=’clerk’ or sal<=2000”,然后单击【执行】按钮,出现如图4.9所示的逻辑或组合查询的结果。
【参见光盘文件】:/第4章/4.2/425-2.sql。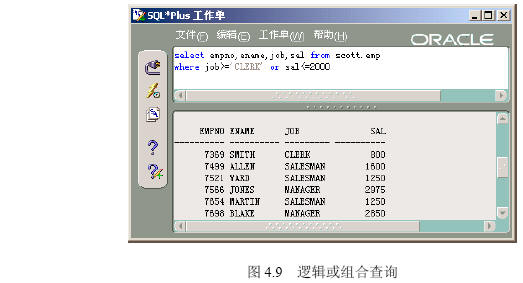
(3)在【命令编辑区】输入“select empno,ename,job from scott.emp where not job=’clerk’”,然后单击【执行】按钮,出现如图4.10所示的逻辑非组合查询的结果。
【参见光盘文件】:/第4章/4.2/425-3.sql。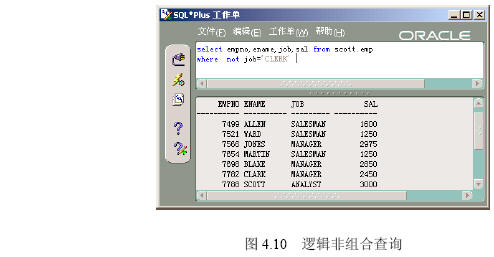
“not job=’clerk’”等价于“job<>’clerk’”。
组合条件中使用的逻辑比较符如表4.2所示。
【参见光盘文件】:/第4章/4.2/table42.sql。
表4.2 逻辑比较符
| 名称 | 实例 |
| and(与) | select * from scott.emp where job=’manager’ and sal<>2000; |
| or (或) | select * from scott.emp where job!=’manager’ or sal<>2000; |
| not(非) | select * from scott.emp where not job>=’manager’; |
4.2.6 排序查询
在【命令编辑区】输入“select empno,ename,job from scott.emp where job<=’clerk’ order by job asc,sal desc”,然后单击【执行】按钮,出现如图4.11所示的排序查询的结果。
【参见光盘文件】:/第4章/4.2/426.sql。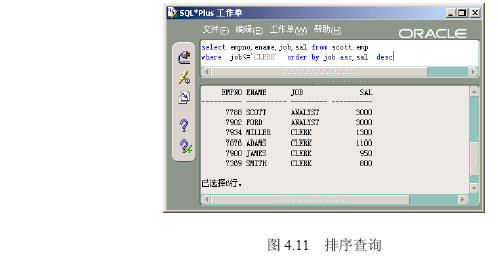
order by 可以指定查询结果如何排序,形式为字段名 排序关键词;asc代表升序排列,desc代表降序排列,多个排序字段之间通过逗号分割。若有where查询条件,order by要放在where语句后面。
4.2.7 分组查询
分组查询是指将查询结果按照字段分组。
(1)在【命令编辑区】输入“select empno,ename,job,sal from scott.emp group by job,empno,ename,sal having sal<=2000”,然后单击【执行】按钮,出现如图4.12所示的分组查询的结果。
【参见光盘文件】:/第4章/4.2/427-1.sql。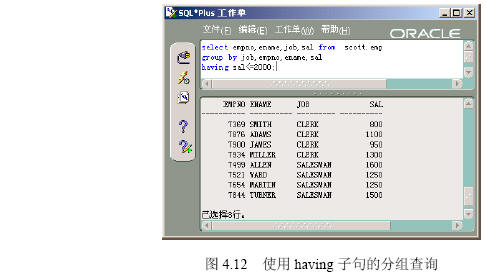
(2)在【命令编辑区】输入“select empno,ename,job,sal from scott.emp where sal<=2000 group by job,empno,ename,sal”,然后单击【执行】按钮,出现如图4.13所示的分组查询的结果。
【参见光盘文件】:/第4章/4.2/427-2.sql。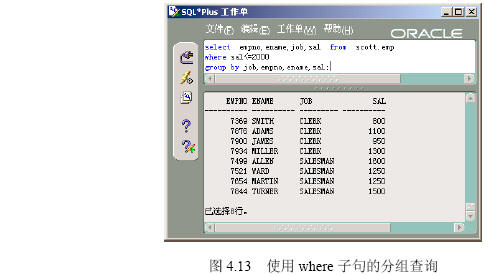
where检查每条记录是否符合条件,having是检查分组后的各组是否满足条件。having语句只能配合group by语句使用,没有group by时不能使用having,但可以使用where。
4.2.8 字段运算查询
可以利用几种基本的算术运算符来查询数据。
常见的+(加)、-(减)、*(乘)、/(除)4种算术运算都可以用来查询数据。
在【命令编辑区】输入“select empno,ename,sal,mgr,sal+mgr from scott.emp”,然后单击【执行】按钮,出现如图4.14所示的结果。
【参见光盘文件】:/第4章/4.2/428.sql。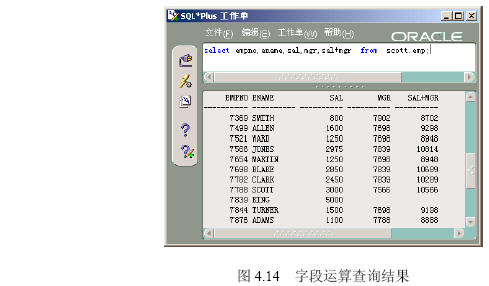
利用算术运算符仅仅适合多个数值型字段或字段与数字之间的运算。
4.2.9 变换查询显示
在【命令编辑区】输入“select empno 编号,ename 姓名,job 工作,sal 薪水 from scott.emp”,然后单击【执行】按钮,出现如图4.15所示的结果,可以将默认的字段名以设定的名称显示。
【参见光盘文件】:/第4章/4.2/429.sql。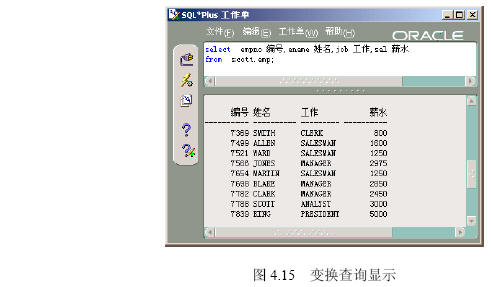
以上我们学习了对单个数据表的查询语句。将上面这些基本的实例经过组合,就可以完成基本的日常数据查询任务,接下来进一步学习多表查询。
新闻热点
疑难解答