什么是模型?
我们的WEB系统一定会和各种数据打交道,实际开发过程中,往往一个类对应了关系数据库的一张或多张数据表,这里就会出现两个问题。
1.类和数据表,一方修改会导致另一方的修改,只要数据表结构不定下来,业务逻辑的开发几乎没法开工
2.获取数据时会牵涉很多SQL语句的拼接,如果数据结构变动,这些SQL需要改写
假如要开发一个博客系统,我们先设计两个Model和两张数据表
第一张数据表,表名是post,存储了博客文章,数据如下:
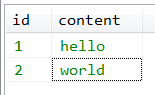
第二章数据表,表名是comment,存储了博客文章的评论,数据如下:
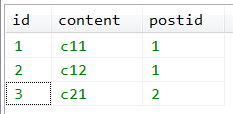
post和comment是一对多的关系,每一篇博客文章对应了多条评论,每一条评论只属于一篇文章。
Model类的设计之前,我们先定义好三个接口
interface IModel{ public static function all(); public static function get($id); public static function where($condition,$value);}定义Model类
class Model implements IModel{ public static $table; public static $db; public function __construct(){ self::$db=new MySQL(); } public static function get($id){ return self::where('id',$id); } public static function where($condition,$value){ $sql=sprintf("select * from %s where %s='%s'",self::$table,$condition,$value); return self::$db->Query($sql); } public static function all(){ $sql=sprintf("select * from %s",self::$table); return self::$db->Query($sql); }}这三个接口分别负责了三种查询:遍历查询,条件查询,按编号查询,其实这三种接口的设计并不是最科学的,甚至get方法不过是where的一种特殊形式,但是这样的设计并不影响我们工程,甚至也有助于理解,我们后期会对这段代码做改动。
之所以在Model类里就完成了SQL的拼接,就是希望在子类中不必重复再写SQL。
然后是Post类的定义
class PostModel extends Model{ public $postid; public function __construct(){ parent::__construct(); parent::$table='post'; }}还有Comment类的定义
class CommentModel extends Model{ public $commentid; public function __construct(){ parent::__construct(); parent::$table='comment'; }}我们可以在控制器的方法中写这样的代码来完成调用数据
$post=new PostModel();$post::all();$arr=$post::get('1');var_dump($arr);$comment=new CommentModel();$arr=$comment::get('2');var_dump($arr);我们发现,这样的代码很简洁,但是问题也随之而来,我们SQL查询时候,还有很多复杂的联表查询如join操作,如此,拼接SQL还是不可避免的,这个复杂的问题,我们放在后面解决。
新闻热点
疑难解答