Python中的关键字是Python的保留字。用户借助这些关键字可以实现程序的相关功能,Python程序解释器通过这些关键字来定义程序的机构,知道用户要实现的程序功能。我们在定义程序的变量、类名及其他Python对象时不能使用这些关键字。
在最新的Python中,共定义了35个关键字。

我们可以使用Python中提供的help()和keywords命令查看这些关键字。
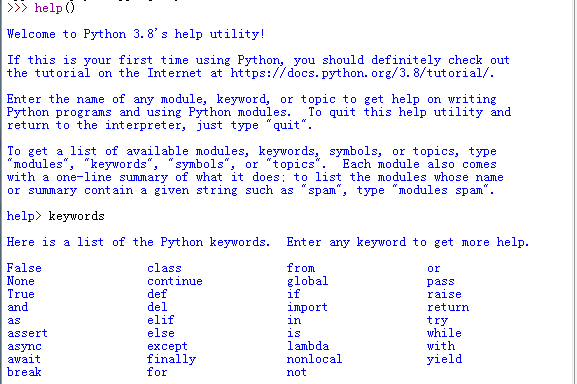
这些关键字的主要用途简单介绍如下:
| 序号 | 关键字 | 用途 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | False | 表示逻辑假 | x = False |
| 2 | class | 用于定义一个类 |
class Student: |
| 3 | from | 用于从某模块中导入类 | from collections import OrderedDict |
| 4 | or | 逻辑运算符:或 | x = True or False |
| 5 | None | NoneType对象的实例,可以简单认为相当于其他语言中的null | x = None |
| 6 | continue | 用于while或for循环中,用于结束本次循环而继续下一次循环 | numbers = range(1,11) for number in numbers: if number == 7: continue |
| 7 | global | 用于定义变量时,可以在在定义变量范围外使用该变量 |
x = 0 |
| 8 | pass | 此关键字表示什么也不做,用于不准备执行任何代码的情形。 | def Sample: pass |
| 9 | True | 表示逻辑值真 | x = True |
| 10 | def | 用于定义一个Python函数 | def MyFunc(): print("www.VeVb.com") |
| 11 | if | 用于表示条件,表示如果,即满足某种条件时要执行其后的语句块 | s = "武林网VEVB" if s == "武林网VEVB": print("http://www.VeVb.com") |
| 12 | raise | 用于程序中抛出一个异常,类似于Java或C#中的throw语句。 | def myFunc(s): if s!="www.VeVb.com": raise Exception("网址不正确。") |
| 13 | and | 逻辑与运算符。 | url = "www.VeVb.com" webname="武林网VEVB" print(url == "www.VeVb.com" and webname == "武林网VEVB") |
| 14 | del | 用于删除一个对象,如变量,列表,类的实例等。 | s = "www.VeVb.com" print(s) del s print(s) #NameError: name "s" is not defined |
| 15 | import | 用于把程序的模块或模块的类导入到当前程序中。 | from collections import OrderedDict |
| 16 | return | 用于函数中带出返回值。 | def Add(x,y): return x+y |
| 17 | as | 用于import,except,with语句中提供一个别名 | from collections import OrderedDict as od |
| 18 | elif | 相当于else if | x = 3 if x > 3: print("比3大")elif x < 3: print("比3小")else: print("等于3") |
| 19 | in | 用于检测集合中的成员 | li = [1,2,3,4,5] if 2 in li : print("OK") |
| 20 | try | 用于处理异常,把可能发生异常的语句放在try块中。 | x = "VeVb.com" try: i = int(x) except:print("error") |
| 21 | assert | assert语句允许我们在程序中插入调试断言。如果断言为真,程序将继续运行。否则抛出AssertionError。 | def divide(x, y): assert b!=0 return a / b |
| 22 | else | 用于if..elif..中,当前边的条件都不满足时,将执行else后的语句 | 见elif的例子 |
| 23 | is | 用于判断两个变量是否具有相同的数据类型,相当于== | fruits = [‘apple’] fruits1 = [‘apple’] f = fruits print(f is fruits) # True print(fruits1 is fruits) # False |
| 24 | while | 循环语句,当条件满足时,会反复执行其语句块。 | x = 1 sum=0 while x<10: sum += x i+=1 print(sum) |
| 25 | async | Python3.5新增的关键字。用于couroutline函数体中,与asyncio模块和await关键字配合使用。 | import asyncio import time async def ping(url): print(f’Ping Started for {url}’) await asyncio.sleep(1) print(f’Ping Finished for {url}’) async def main(): await asyncio.gather( ping(‘askpython.com’), ping(‘python.org’), ) if __name__ == ‘__main__’: then = time.time() loop = asyncio.get_event_loop() loop.run_until_complete(main()) now = time.time() print(f’Execution Time = {now – then}’) |
| 26 | await | Python3.5中新增的关键字。用于异步处理。 | 参见async中的例子 |
| 27 | lambda | 用于创建lambda表达式。 |
multiply = lambda a, b: a * b |
| 28 | with | 用于定义了管理器的上下文中,执行相关的语句块。这类对象必须实现了__enter__()和__exit__()函数。 | with open(‘data.csv’) as file: file.read() |
| 29 | except | 用于捕获try块抛出的异常。 | 见try的例子 |
| 30 | finally | 用于try..except异常处理,放在finally块中的语句不管异常是否发生都会被执行,常用语回收释放资源等。 | def division(x, y): try: return x / y except ZeroDivisionError as e: print(e) return -1 finally: print(‘this will always execute’) print(division(10, 2)) print(division(10, 0)) |
| 31 | nonlocal | 用于访问语句块外的变量。 | def outer(): v = ‘outer’ def inner(): nonlocal v v = ‘inner’ inner() print(v) outer() |
| 32 | yield | 用于函数体中,逐个返回每个值。 |
def multiplyByTen(*kwargs): |
| 33 | break | 用于for循环或while循环,用于终止包含此关键字最近循环的整个循环。 | i = 1 while i < 100: i+=1 if(i>50): break; |
| 34 | for | for循环 | sum = 0 for i in range(101): sum += i print(sum) |
| 35 | not | 逻辑非 | i = not True |
新闻热点
疑难解答