1.概念
双向链表也叫双链表,是链表的一种,它的每个数据结点中都有两个指针,分别指向直接后继和直接前驱。所以,从双向链表中的任意一个结点开始,都可以很方便地访问它的前驱结点和后继结点。一般我们都构造双向循环链表。
结构图如下所示:
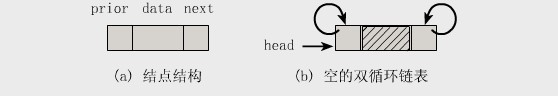
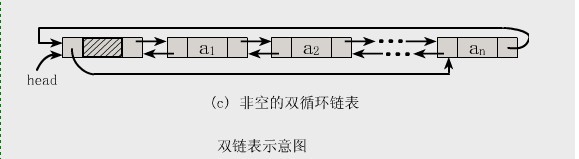
2.基本操作实例
DoubleList.cpp
#include "stdafx.h"#include "DoubleList.h"#include <stdio.h>#include <malloc.h>#include <stdlib.h>DoubleList::DoubleList(){ pDoubleListNode pDouList = NULL; // 创建双链表 CreateDouList(pDouList); PrintDouList(pDouList); // 打印逆序链表 PrintDouReverseList(pDouList); // 节点后插入节点 InsertNodeAfter(pDouList); PrintDouList(pDouList); // 节点前插入节点 InsertNodeBefore(pDouList); PrintDouList(pDouList); // 删除节点 DeleteNode(pDouList); PrintDouList(pDouList); // 删除链表 DeleteDouList(pDouList); PrintDouList(pDouList); system("PAUSE");}DoubleList::~DoubleList(){}//创建双向链表void DoubleList::CreateDouList(pDoubleListNode &head){ char x; // 定义成char型是用于输入'q'时可以退出,其实定义成int也能退出 pDoubleListNode p, s; head = (pDoubleListNode)malloc(sizeof(DoubleListNode)); head->next = NULL; head->prior = NULL; // 构造头结点p p = head; printf("/n输入双向链表的元素,每输入一个元素后按回车,输入q表示结束./n"); fflush(stdin); //清空输入缓冲区 x = getchar(); while (x != 'q') { s = (pDoubleListNode)malloc(sizeof(DoubleListNode)); s->data = x - '0'; // 得到的是输入字符的ASCII码,减去30H就变成想要的数字 s->next = NULL; s->prior = p; p->next = s; p = s; fflush(stdin); x = getchar(); } if (x == 'q') { printf("双向链表构造完毕!/n"); }}//打印双向链表void DoubleList::PrintDouList(pDoubleListNode &head){ pDoubleListNode p; printf("/n打印出双向链表数据为:/n"); if (!IsDouListEmpty(head)) { p = head->next; while (p) { printf("%d/n", p->data); p = p->next; } }}//逆序打印双向链表void DoubleList::PrintDouReverseList(pDoubleListNode &head){ pDoubleListNode p; printf("/n打印出逆序双向链表数据为:/n"); if (!IsDouListEmpty(head)) { p = head->next; while (p->next) { p = p->next; } while (p->prior) { printf("%d /n", p->data); p = p->prior; } }}//求链表长度int DoubleList::GetDouListLength(pDoubleListNode &head){ int length = 0; if (head == NULL) { printf("链表不存在,请先初始化!/n"); } else { pDoubleListNode p = head->next; while (p) { length++; p = p->next; } } return length;}//判断链表是否为空bool DoubleList::IsDouListEmpty(pDoubleListNode &head){ if (head == NULL) { printf("链表不存在,请先初始化!/n"); return true; } else if (head->next == NULL) { printf("链表为空!/n"); return true; } return false;}//把双向链表置空void DoubleList::ClearDouList(pDoubleListNode &head){ if (head == NULL) { printf("链表不存在,请先初始化!/n"); } else { pDoubleListNode p, q; p = q = head->next; //是p、q指向第一个元素 head->next = NULL; while (p) //逐个释放元素所占内存 { p = p->next; free(q); q = p; } }}// 删除双向链表void DoubleList::DeleteDouList(pDoubleListNode &head){ printf("/n删除双向链表/n"); ClearDouList(head); free(head); head = NULL;}// 在双向链表中第i个位置后面插入元素void DoubleList::InsertNodeAfter(pDoubleListNode &head){ int data, pos; pDoubleListNode p, s; p = head; int i = 0; printf("/n在双向链表中第i个位置后面插入元素/n"); printf("请输入要插入的元素和位置:/n"); scanf_s("%d%d", &data, &pos, 100); if (head == NULL) { printf("链表不存在,请先初始化!/n"); } else if (head->next == NULL) { printf("链表为空,插入第一个元素!/n"); s = (pDoubleListNode)malloc(sizeof(DoubleListNode)); s->data = data; s->prior = NULL; s->next = NULL; head->next = s; // 将新结点插入head后 } else if (pos<1 || pos>GetDouListLength(head) + 1) { printf("插入位置错误!/n"); } else { while (i < pos) { p = p->next; i++; } if (i == GetDouListLength(head)) //如果在最后一个元素后面插入data { s = (pDoubleListNode)malloc(sizeof(DoubleListNode)); s->data = data; s->next = NULL; s->prior = p; p->next = s; } else { s = (pDoubleListNode)malloc(sizeof(DoubleListNode)); s->data = data; s->next = p->next; p->next->prior = s; p->next = s; s->prior = p; } }}// 在双向链表中第i个位置前面插入元素void DoubleList::InsertNodeBefore(pDoubleListNode &head){ int data, pos; pDoubleListNode p, s; p = head; int i = 0; printf("/n在双向链表中第i个位置前面插入元素/n"); printf("请输入要插入的元素和位置:/n"); scanf_s("%d%d", &data, &pos, 100); if (head == NULL) { printf("链表不存在,请先初始化!/n"); } else if (head->next == NULL) { printf("链表为空,插入第一个元素!/n"); s = (pDoubleListNode)malloc(sizeof(DoubleListNode)); s->data = data; s->prior = NULL; s->next = NULL; head->next = s; // 将新结点插入head后 } else if (pos<1 || pos>GetDouListLength(head) + 1) { printf("插入位置错误!/n"); } else { while (i < pos) { p = p->next; i++; } if (i == 1) // 如果在第一个元素前面插入data { s = (pDoubleListNode)malloc(sizeof(DoubleListNode)); s->data = data; head->next = s; // 将新结点插入head后 s->prior = head; // 新结点的前结点指向头结点 s->next = p; // 新结点的后结点指向原head的后结点 p->prior = s ; // 原第一个结点的前结点指向新结点 } else { s = (pDoubleListNode)malloc(sizeof(DoubleListNode)); s->data = data; s->prior = p->prior; s->next = p; p->prior->next = s; p->prior = s; } }}//删除双向链表中的第i个元素void DoubleList::DeleteNode(pDoubleListNode &head){ int pos; int i = 0; pDoubleListNode p = head; printf("/n在双向链表中删除第i个位置的元素/n"); printf("请输入要删除的位置:"); scanf_s("%d", &pos, 100); if (IsDouListEmpty(head)) { return; } else if (pos<1 || pos>GetDouListLength(head)) { printf("删除的位置不存在!/n"); } else { while (i < pos) { p = p->next; i++; } if (i == GetDouListLength(head)) { p->prior->next = NULL; free(p); } else { p->prior->next = p->next; p->next->prior = p->prior; free(p); } }}DoubleList.h
#pragma oncetypedef struct DoubleListNode{ int data; //数据 struct DoubleListNode *prior; //前驱 struct DoubleListNode *next; //后继}DoubleListNode, *pDoubleListNode;class DoubleList{public: DoubleList(); ~DoubleList(); //初始化双向链表 void DoubleList::CreateDouList(pDoubleListNode &head); //打印双向链表 void DoubleList::PrintDouList(pDoubleListNode &head); //逆序打印双向链表 void DoubleList::PrintDouReverseList(pDoubleListNode &head); //求链表长度 int DoubleList::GetDouListLength(pDoubleListNode &head); //判断链表是否为空 bool DoubleList::IsDouListEmpty(pDoubleListNode &head); //把双向链表置空 void DoubleList::ClearDouList(pDoubleListNode &head); //删除双向链表 void DoubleList::DeleteDouList(pDoubleListNode &head); //在双向链表中第i个位置后面插入元素m void DoubleList::InsertNodeAfter(pDoubleListNode &head); // 在双向链表中第i个位置前面插入元素 void DoubleList::InsertNodeBefore(pDoubleListNode &head); //删除双向链表中的第i个元素 void DoubleList::DeleteNode(pDoubleListNode &head);};3.对链表插入节点的理解
例如在节点i前插入一个新的节点(即上面代码中的InsertNodeBefore函数):
typedef struct DoubleListNode{ int data; // 数据 struct DoubleListNode *prior; // 前驱 struct DoubleListNode *next; // 后继}DoubleListNode, *pDoubleListNode;假设该链表由五个节点构成,分别为A,B,C,D,E
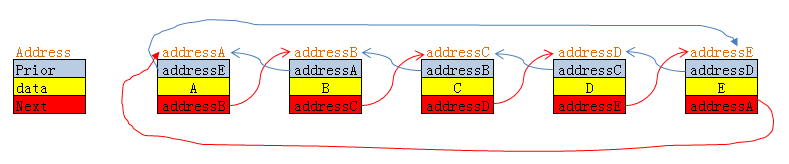
图中假设了A,B,C,D,E的地址分别为:addressA,addressB,addressC,addressD,addressE。
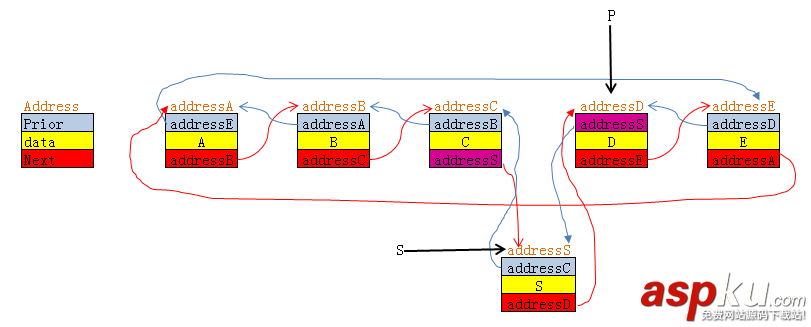
下面将分析链表的前插的例子:
双链表的前插,下面这是在节点"D"前插入一个新的节点"S"的代码和分析
以上这篇C++ 双链表的基本操作(详解)就是小编分享给大家的全部内容了,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持VEVB武林网。
新闻热点
疑难解答