8.编写代码类
每个分离的函数可以执行一个明确的任务。任务越简单,编写与测试这个函数就越简单,当然也不要将这个函数分得太小——若将程序分成太多的小个体,读起来就会很困难。
使用继承可以重载操作。我们可以替换成一个大的Display()函数,但是改变整个页面的显示方式几乎是不可能的。将显示功能分成几个独立的任务则更好,这样我们可以只需重载需要改变的部分。
如下所示的page类提供了简单灵活的方法来创建页面:
<?phphtml' target='_blank'>class Page{ // class Page's attributes public $content; //页面的主要内容 public $title = 'TLA Consulting Pty Ltd'; //页面的标题 public $keywords = 'TLA Consulting, Three Letter Abbreviation, some of my best friends are search engines'; //metatags便于搜索引擎对其检索 public $buttons = array('Home' => 'home.php', 'Contact' => 'contact.php', 'Services' => 'services.php', 'Site Map' => 'map.php' ); //使用一个数组来保存按钮的文本标签以及该按钮指向的URL // class Page's operations public function __set($name, $value) { $this->$name = $value; } //可以从定义访问函数来设置和获得已定义的变量值开始 public function Display() { echo '<html><head>'; $this -> DisplayTitle(); $this -> DisplayKeywords(); $this -> DisplayStyles(); echo '</head><body>'; $this -> DisplayHeader(); $this -> DisplayMenu($this->buttons); echo $this->content; $this -> DisplayFooter(); echo '</body></html>'; } public function DisplayTitle() { echo '<title>'.$this->title.'</title>'; } public function DisplayKeywords() { echo '<meta name='keywords' content=''.$this->keywords.''/>'; } public function DisplayStyles() { ?> <style> h3 { color:white; font-size:24pt; text-align:center; font-family:arial,sans-serif } .menu { color:white; font-size:12pt; text-align:center; font-family:arial,sans-serif; font-weight:bold } td { background:black } p { color:black; font-size:12pt; text-align:justify; font-family:arial,sans-serif } p.foot { color:white; font-size:9pt; text-align:center; font-family:arial,sans-serif; font-weight:bold } a:link,a:visited,a:active { color:white } </style><?php } public function DisplayHeader() { ?> <table width='100%' cellpadding='12' cellspacing='0' border='0'> <tr bgcolor ='black'> <td align ='left'><img src = 'logo.gif' /></td> <td> <h3>TLA Consulting Pty Ltd</h3> </td> <td align ='right'><img src = 'logo.gif' /></td> </tr> </table><?php } public function DisplayMenu($buttons) { echo '<table width='100%' bgcolor='white' cellpadding='4' cellspacing='4'>'; echo '<tr>'; //calculate button size $width = 100/count($buttons); while (list($name, $url) = each($buttons)) { $this -> DisplayButton($width, $name, $url, !$this->IsURLCurrentPage($url)); } echo '</tr>'; echo '</table>'; } public function IsURLCurrentPage($url) { if(strpos($_SERVER['PHP_SELF'], $url )==false) { return false; } else { return true; } } public function DisplayButton($width,$name,$url,$active = true) { if ($active) { echo '<td width = ''.$width.'%'> <a href=''.$url.''> <img src='s-logo.gif' alt=''.$name.'' border='0' /></a> <a href=''.$url.''><span class='menu'>'.$name.'</span></a> </td>'; } else { echo '<td width=''.$width.'%'> <img src='side-logo.gif'> <span class='menu'>'.$name.'</span> </td>'; } } public function DisplayFooter() {?><table width='100%' bgcolor='black' cellpadding='12' border='0'><tr><td> <p class='foot'>© TLA Consulting Pty Ltd.</p> <p class='foot'>Please see our <a href =''>legal information page</a></p></td></tr></table><?php }}?>
请注意函数DisplayStyles()、DisplayHeader()和DisplayFooter()需要显示没有经过PHP处理的大量静态HTML。因此,我们简单地使用了PHP结束标记(?>)、输入HTML,然后再在函数体内部使用一个PHP打开标记(<?php)。
操作IsURLCurrentPage()将判断按钮URL是否指向当前页。
这里,我们使用了字符串函数strpos(),它可以查看给定的URL是否包含在服务器设置的变量中。strpos($__SERVER[‘PHP_SELF’], $url)语句将返回一个数字(如果$url中的字符串包含在全局变量$_SERVER[‘PHP_SELF’])或者false(如果没有包含在全局变量中)。
首页使用page类完成生成页面内容的大部分工作:
<?php require('page.inc'); $homepage = new Page(); $homepage->content ='<p>Welcome to the home of TLA Consulting. Please take some time to get to know us.</p> <p>We specialize in serving your business needs and hope to hear from you soon.</p>'; $homepage->Display();?>在以上的程序清单中可以看出,如果使用Page类,我们在创建新页面的时候只要做少量工作。通过这种方法使用类意味着所有页面都必须很相似。
如果希望网站的一些地方使用不同的标准页,只要将page.inc复制到名为page2.inc的新文件里,并做一些改变就可以了。这意味着每一次更新或修改page.inc时,要记得对page2.inc进行同样的修改。
一个更好的方法是用继承来创建新类,新类从Page类里继承大多数功能,但是必须重载需要修改的部分。
Services页面继承了Page类,但是重载了Display()操作,从而改变了其输出结果:
<?php require ('page.inc'); class ServicesPage extends Page { private $row2buttons = array( 'Re-engineering' => 'reengineering.php', 'Standards Compliance' => 'standards.php', 'Buzzword Compliance' => 'buzzword.php', 'Mission Statements' => 'mission.php' ); public function Display() { echo '<html><head>'; $this -> DisplayTitle(); $this -> DisplayKeywords(); $this -> DisplayStyles(); echo '</head><body>'; $this -> DisplayHeader(); $this -> DisplayMenu($this->buttons); $this -> DisplayMenu($this->row2buttons); echo $this->content; $this -> DisplayFooter(); echo '</body></html>'; } } $services = new ServicesPage(); $services -> content ='<p>At TLA Consulting, we offer a number of services. Perhaps the productivity of your employees would improve if we re-engineered your business. Maybe all your business needs is a fresh mission statement, or a new batch of buzzwords.</p>'; $services -> Display();?>通过PHP类创建页面的好处是显而易见的,通过用类完成了大部分工作,在创建页面的时候,我们就可以做更少的工作。在更新页面的时候,只要简单地更新类即可。通过继承,我们还可从最初的类派生出不同版本的类而不会破坏这些优势。
不过,用脚本创建网页要求更多计算机处理器的处理操作,应该尽量使用静态HTML网页,或者尽可能缓存脚本输出,从而减少在服务器上的载入操作。
9.PHP面向对象的高级功能
9.1 使用Pre-Class常量
可以在不需要初始化该类的情况下使用该类中的常量
class Math { const pi = 3.14159; //定义常量}echo Math::pi;可以通过使用::操作符指定常量所属的类来访问Per-Class常量。
9.2 实现静态方法
和Pre-Class常量的思想一样,可以在未初始化类的情况下直接调用这个方法,不过,在这个静态方法中,不允许使用this关键字,因为可能会没有可以引用的对象。
class Math { static function squared($input) { return $input * $input; }}echo Math::squared(8);9.3 检查类的类型和类型提示
instanceof关键字允许检查一个对象的类型。可以检查一个对象是否是特定类的实例,是否是从某个类继承过来或者是否实现了某个接口。
另外,类型检查等价于instanceof的作用。
function check_hint(B $someclass){ // ...}以上示例将要求$someclass必须是类B的实例。如果按如下方式传入了类A的一个实例:
check_hint($a);
将产生如下所示的致命错误:
Fatal error: Argument 1 must be an instance of B
9.4 延迟静态绑定
PHP 5.3版本引入了延迟静态绑定(late static binding)的概念,该特性允许在一个静态继承的上下文对一个被调用类的引用。父类可以使用子类重载的静态方法。如下所示的是PHP手册提供的延迟静态绑定示例:
<?phpclass A{ public static function who(){ echo __CLASS__; } public static function test(){ static::who(); // Here comes Late Static Bindings }}class B extends A{ public static function who(){ echo __CLASS__; }}B::test();?>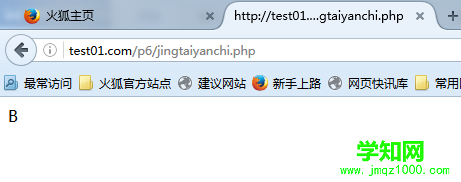
通俗的说,就是B通过继承走的A里的test(),然后通过静态延迟走的B里重载的who()。
无论类是否被重载,允许在运行时调用类的引用将为你的类提供更多的功能。
9.5克隆对象
PHP提供了clone关键字,该关键字允许复制一个已有的对象。
$c = clone $b;
将创建与对象$b具有相同类的副本,而且具有相同的属性值。
当然,可以自己在类中重新定义__clone函数,来控制克隆的过程。
9.6 使用抽象类
PHP提供了抽象类。这些类不能被实例化,同样类方法也没有实现,只是提供类方法的声明,没有具体实现。
abstract operationX($param1, $param2);
包含抽象方法的任何类自身必须是抽象的。
抽象方法和抽象类主要用于复杂的类层次关系中,该层次关系需要确保每一个子类都包含并重载了某些特性的方法,这也可以通过接口来实现。
9.7 使用__call()重载方法
在PHP中,__call()方法用来实现方法的重载。
<?phpclass overload { public function displayArray($array) { foreach($array as $print) { echo $print; echo '<br />'; } } public function displayScalar($scalar) { echo $scalar; echo '<br />'; } public function __call($method, $p) { if ($method == 'display') { if (is_object($p[0])) { $this->displayObject($p[0]); } else if (is_array($p[0])) { $this->displayArray($p[0]); } else { $this->displayScalar($p[0]); } } }}$ov = new overload;$ov->display(array(1, 2, 3));$ov->display('cat'); ?>
__call()方法必须带有两个参数。第一个包含了被调用的方法名称,而第二个参数包含了传递给该方法的参数数组。
使用__call方法,不需要实现任何display()方法。
9.8 使用__autoload()方法
__autoload()函数将在实例化一个还没有被声明的类时自动调用。
__autoload()方法的主要用途是尝试包含或请求任何用来初始化所需类的文件。
9.9 实现迭代器和迭代
可以使用foreach()方法通过循环方式取出一个对象的所有属性,就像数组方式一样。
<?phpclass myClass{ public $a = '5'; public $b = '7'; public $c = '9';}$x = new myClass;foreach($x as $attribute){ echo $attribute.'<br />';}?>
如果需要一些更加复杂的行为,可以实现一个iterator(迭代器)。要实现一个迭代器,必须将要迭代的类实现IteratorAggregare接口,并且定义一个能够返回该迭代类实例的getIterator方法。这个类必须实现Iterator接口,该接口提供了一系列必须实现的方法。
迭代器和迭代的示例基类:
<?phpclass ObjectIterator implements Iterator { //迭代器 这个类实现了interator接口 private $obj; private $count; private $currentIndex; function __construct($obj) { $this->obj = $obj; $this->count = count($this->obj->data); } function rewind() { $this->currentIndex = 0; } function valid() { return $this->currentIndex < $this->count; } function key() { return $this->currentIndex; } function current() { return $this->obj->data[$this->currentIndex]; } function next() { $this->currentIndex++; }}class Object implements IteratorAggregate //接口{ public $data = array(); function __construct($in) { $this->data = $in; } function getIterator() { return new ObjectIterator($this); //返回迭代示例的方法 }}$myObject = new Object(array(2, 4, 6, 8, 10));$myIterator = $myObject->getIterator();for($myIterator->rewind(); $myIterator->valid(); $myIterator->next()){ $key = $myIterator->key(); $value = $myIterator->current(); echo $key.' => '.$value.'<br />';}?>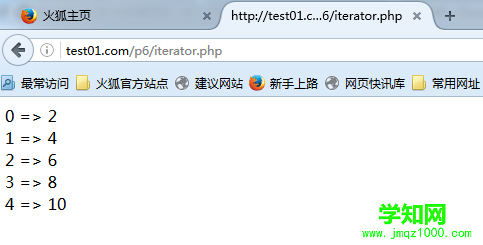
ObjectIterator类具有Iterator接口所要求的一系列函数:
· 构造函数并不是必需的,但是很明显,它是设置将要迭代的项数和当前数据项链接的地方。
· rewind()函数将内部数据指针设置回数据开始处。
· valid()函数将判断数据指针的当前位置是否还存在更多数据。
· key()函数将返回数据指针的值。
· value()函数将返回保存在当前数据指针的值。
· next()函数在数据中移动数据指针的位置。
像这样使用Iterator类的原因就是即使潜在的实现发生了变化,数据的接口还是不会发生变化。
9.10 将类转换成字符串
__toString()函数的所有返回内容都将被echo语句打印。
<?php$p = new Printable;echo $p;class Printable{ public $testone; public $testtwo; public function __toString(){ return(var_export($this, TRUE)); }}?>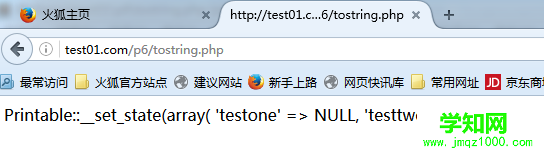
var_export()函数打印出了类中的所有属性值。
9.11 使用Reflection(反射)API
PHP的面向对象引擎还包括反射API。反射是通过访问已有类和对象来找到类和对象的结构和内容的能力。
显示关于Page类的信息:
<?phprequire_once('page.inc');$class = new ReflectionClass('Page');echo '<pre>'.$class.'</pre>';?>
这里使用了Reflection类的__toString()方法来打印这个数据。注意,<pre>标记位于不同的行上,不要与__toString()方法混淆。
PHP编程郑重声明:本文版权归原作者所有,转载文章仅为传播更多信息之目的,如作者信息标记有误,请第一时间联系我们修改或删除,多谢。
新闻热点
疑难解答